On the future of bike lanes in Metro Manila and other cities and municipalities in the Philippines
My friends and I were talking about the current buzz about the bike lanes including statements made by certain personalities (influencers, advocates, government officials, etc.) about biking and bike lanes. There were many recent pronouncements of motorcycles being allowed to use bike lanes or the outright removal of bike lanes. We all agreed this was backward and the way forward is to build on the current network and facilities. What we have in our cities and municipalities are not perfect and far from ideal but they are a start and perhaps the foundation for a bikeway network that can eventually make a dent on the car-centric transportation we have.
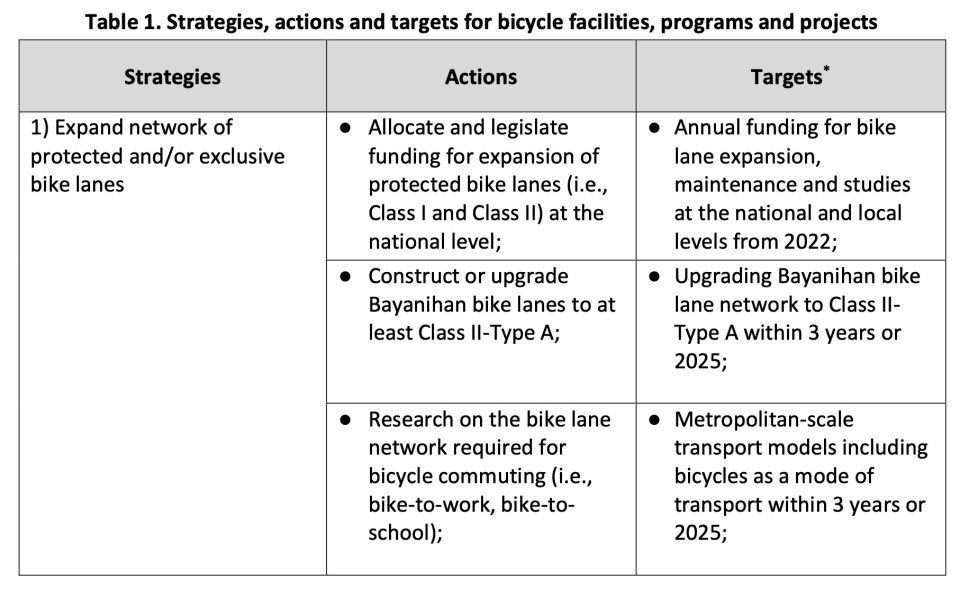
I share below the strategies, actions and targets for bicycle facilities, programs and projects from the Network Planning for the Establishment of Bike Lanes in Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao that was completed middle of 2022. The project is DOTr’s with support from the UNDP. The table is from the Final Report of the project.


A Happy Christmas to all!
–
Shared article: Active and Micro Mobility Modes Can Provide Cost-Effective Emission Reductions–If We Let Them
I’m sharing this article on active and micro mobility modes from Todd Litman, published in Planetizen.com:
Source: Active and Micro Mobility Modes Can Provide Cost-Effective Emission Reductions–If We Let Them
From the article:
“Common Active Transportation Leverage Effects:
–Shorter trips. Shorter active trips often substitutes for longer motorized trips, such as when people choose a local store rather than driving to more distant shops.
–Reduced chauffeuring. Better walking and bicycling conditions reduces the need to chauffeur non-drivers (special trips to transport a passenger). These often require empty backhauls (miles driven with no passenger). As a result, each mile of avoided chauffeuring often reduces two vehicle-miles.
-Increased public transit travel. Since most transit trips include walking and bicycling links, improving these modes supports public transit travel and transit-oriented development.
-Vehicle ownership reductions. Active mode improvements allow some households to reduce their vehicle ownership, which reduces vehicle trip generation, and therefore total vehicle-miles.
-Lower traffic speeds. Active travel improvements often involve traffic speed reductions. This makes non-auto travel more time-competitive with driving and reduces total automobile travel.
-More compact development. Walking and bicycling support more compact, multimodal communities by reducing the amount of land devoted to roadways and parking, and creating more attractive streets.
-Social norms. As active travel increases, these modes become more socially acceptable.
The article is a must read if we are to understand how important active transport and micro mobilities are in the context of today’s transport conundrum. Of course, part of the contextualization and perhaps ‘localization’ on these modes will be related to land use or development. The latter is a big challenge especially for the likes of Metro Manila and other rapidly developing cities in the Philippines where housing in the cities (related to compact development) has become quite expensive and has driven more and more people to live in the suburbs. As I’ve mentioned in previous posts, this has resulted in more pressure to develop transportation systems but infrastructure development cannot play the catch up game given the limited resources for their construction. Meanwhile, services are also behind in terms of quality and requires reforms and rationalizations.
–
On Metro Manila having one of the worst transit systems in the world
This is a follow-up to the previous post on the UC-Berkeley Study. Here is an example of how media featured the study outcomes:
https://www.facebook.com/CNNPhilippines/videos/1089453421728393
I didn’t see whether there was a response from government. These studies end up as features and nothing more if these do not prompt or push authorities to act on the problem. Even experts from academe or industry are reduced to being commentators or even pundits providing context, assessments and opinions, even recommendations that are perceived to fall on deaf ears. Perhaps government is already desensitized about these issues and will just trudge along at its own pace? In the end, it is the commuters mostly taking public transportation who continue to suffer and lose productive time to their daily travels.
–
On the best public transit systems in the world
Manila’s poor ranking in recent study conducted by the University of California Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies with think tank Oliver Wynam on public transit systems caught the attention of a lot of people. Media was quick to feature this in the news and I am aware of at least GMA and CNN Philippines doing features of this in their news programs. Here is the article on the same that mentions the UC Berkeley ITS study:
Pollard, A. (November 21, 2022 ) “These Cities Have the Best Public Transit Systems,” Bloomberg CityLab, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-11-21/these-cities-have-the-best-public-transit-systems [Last accessed: 12/11/2022]
Manila, or Metro Manila to be exact, placed only 56th in public transit while ranking 48th in sustainable mobility and 58th in urban mobility readiness. I leave it to the readers to go read the UC Berkeley report rather than depending on media or social med influencers for their takes on the ranking. The report can be downloaded from the link I provided above.
Perhaps there should be an assessment of cities (at least the highly urbanized ones) in the Philippines to see how they are ranked. There should be a criteria (UC Berkeley and Oliver Wynam used distance to public transit, affordability, operating hours, crowding and commute speeds among others in their study) to be agreed upon where experts can score cities using a simple-enough scale, say 1 to 10 with 10 being the highest score. What are your top 5 Philippine cities in terms of public transportation?
–
On guerilla tactics in urbanism – guerilla crosswalks
I am sharing this article on guerilla crosswalks in the US. It is interesting as communities or groups concerned with road safety decided to put up interventions (in this case crosswalks) in order to address safety concerns pertaining to pedestrian ROW along roads. In most if not all countries, pedestrians are limited where they may cross and there are jaywalking laws and penalties that are now being regarded as car-centric policies that need to be revised to favor pedestrians more than motor vehicles.
Zipper, D. (December 1, 2022) “The Case for Guerrilla Crosswalks,” Bloomberg CityLab, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-12-01/when-crosswalks-go-rogue [Last accessed: 12/10/2022]
To quote from the article:
“Such acts of unsanctioned “tactical urbanism” are of a kin to many other DIY street interventions, such as pop-up bike lanes. But they are not without risks. Affluent communities could have more residents willing to volunteer time and resources, for example, even though pedestrian deaths are concentrated in low-income neighborhoods. “The locations identified by guerrilla crosswalk activists may or may not coincide with where the planners and engineers have identified as highest need,” said Sam Zimbabwe, the former director of Seattle DOT.
But in Los Angeles, the Crosswalk Collective spokesperson said that the group is “always mindful of who has access to safety installations and who doesn’t,” adding that all its crosswalks to date have been sited in low- and moderate-income neighborhoods of Central and East Los Angeles.
Zimbabwe also noted the limited benefits of paint on faster roads (which the Federal Highway Administration has documented): “Particularly on multilane arterials, only marking a crosswalk without deploying other tools does not address the ‘multiple threat’ problem, where one driver stops but the driver in another lane does not.“ (The Crosswalk Collective spokesperson agreed, saying that the group rejects proposed locations due to safety concerns “all the time.”)
But in the right setting, unauthorized street infrastructure additions can lead to one of two outcomes — and both are constructive. One possibility is that the city removes it, in which case media attention and resident backlash put pressure on local officials to be more responsive to safety requests. (That coverage may also compel more residents to join street safety groups).
The other option is that city officials take the hint and accept what residents have built. Eight years ago, Seattle transportation planner Dongho Chang won the enduring appreciation of local cyclists when he responded to a pop-up bike lane first by thanking activists for their passion, and then by making the bike lane permanent. Now working with the Washington State Department of Transportation, Chang does not share Seattle DOT’s rigid opposition to guerrilla crosswalks. “It would be good to acknowledge the effort that was done by the residents,” he said. “If there is a way to keep the crosswalk, it would be ideal to try to do that.”“
–
This is, of course, in the US where such tactical urbanism might be in vogue in certain cities and communities. Would such be allowed or encouraged in the Philippines? Actually, there are already many cases where tactical urbanism has been applied and usually at the community or barangay level. Prior to the DPWH putting in rumble strips at the approaches of schools, junctions and other locations perceived to be accident or crash prone, people have devised ways to slow down traffic in favor of pedestrian crossings. These include laying down old rubber tires cut and stretched to become humps. There are also barriers laid out to form something like an obstacle course; forcing vehicles to zig-zag instead of going straight along critical sections. These have allowed schoolchildren to cross safe in school zones and pedestrians crossing safely at intersections.
–
On intersection treatments for bicycles
With the increasing popularity of bicycles as a mode of transport particularly for commuting (e.g., bike-to-work, bike-to-school), we should be redesigning our intersections to include elements essential for the safety of all users, whether on motorized or non-motorized modes. Here is a short but very informative article on how a simple intersection treatment can significantly improve safety for everyone especially cyclists and pedestrians:
Grief, N. (December 2, 2022) “How Green Paint Can Save Cyclists’ Lives,” Bicycling.com, https://www.bicycling.com/news/a42124210/bike-boxes-intersections/ [Last accessed: 12/3/2022]
To quote from the article:
“A bike box, on the other hand, seems to be the ideal middle ground and the option of the three that these researchers recommend. Cyclists feel more comfortable when compared to the free-for-all of a mixing zone because they have a designated area to be and they’re out ahead of vehicles, but according to the eye movement analysis, they remain alert and watchful for vehicles.”
Here are a couple of drawings showing bike boxes at intersections from the recent Bike Lanes Master Plan for Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao that was developed by DOTr with assistance from the UNDP:
 Bike boxes on a typical three-leg intersection (DOTr and UNDP, 2022)
Bike boxes on a typical three-leg intersection (DOTr and UNDP, 2022)
 Bike boxes on a typical four-leg intersection (DOTr and UNDP, 2022)
Bike boxes on a typical four-leg intersection (DOTr and UNDP, 2022)
The preceding drawings adhere to the DPWH design guidelines that mainly follow AASHTO Guidelines. Of course, there are other design references such as NACTO and the manuals of other countries (e.g., Netherlands, Australia, Singapore, etc.) were the best practice designs can be adopted for local applications.
–
Departure via Mactan Cebu International Airport Terminal 2 – Part 1
The MCIA has two terminals with the newer Terminal 2 being lauded as one of the best designed terminals in the country. It has been recognized internationally, too. And this is mainly due to the architecture of the new terminal.
 Approach ramp to the departure level of MCIA Terminal 2
Approach ramp to the departure level of MCIA Terminal 2
 Departure level driveway – the area looks spacious but you wonder how it is during the peak season.
Departure level driveway – the area looks spacious but you wonder how it is during the peak season.
 The view upon alighting from the vehicle that took us to the airport – note the advisory stating Cebu Pacific departures are via the old Terminal 1.
The view upon alighting from the vehicle that took us to the airport – note the advisory stating Cebu Pacific departures are via the old Terminal 1.
 The walkway leading to the terminal building is very spacious.
The walkway leading to the terminal building is very spacious.
 Passengers may use the baggage trolley for their convenience in hauling their luggage.
Passengers may use the baggage trolley for their convenience in hauling their luggage.
 There are seats for travelers and their well-wishers.
There are seats for travelers and their well-wishers.
 One of the kiosks along the corridor leading to the terminal building
One of the kiosks along the corridor leading to the terminal building
 The view from the walkway shows the Waterfront Hotel with its tiled roofs and the older MCIA Terminal 1 building (at right in the photo).
The view from the walkway shows the Waterfront Hotel with its tiled roofs and the older MCIA Terminal 1 building (at right in the photo).
 A local coffee shop operates out of one of the outdoor kiosks. These kiosks serve both travelers and well-wishers.
A local coffee shop operates out of one of the outdoor kiosks. These kiosks serve both travelers and well-wishers.
 Inside, a popular souvenir shop welcomes travelers.
Inside, a popular souvenir shop welcomes travelers.
 Schedule of departures are shown on one of the screens inside the terminal building.
Schedule of departures are shown on one of the screens inside the terminal building.
 Info booths of some of the airlines using Terminal 2
Info booths of some of the airlines using Terminal 2
 The Terminal 2 building offers very impressive architectural details.
The Terminal 2 building offers very impressive architectural details.
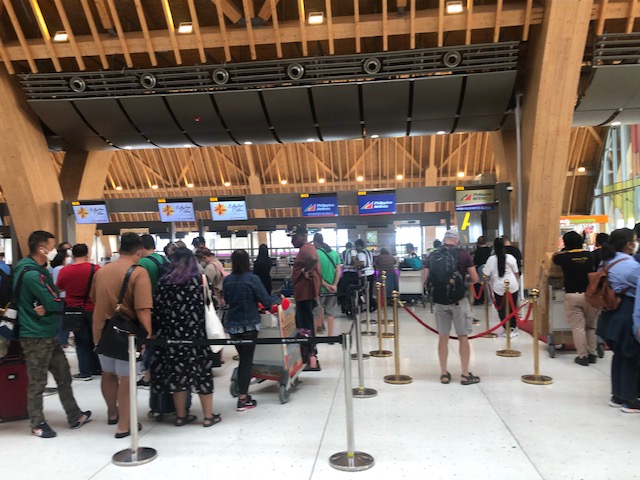 There were long lines not because the airport is crowded but because there were few check-in counters open. Even those who have checked-in online and were to drop-off their bags were not spared the queues.
There were long lines not because the airport is crowded but because there were few check-in counters open. Even those who have checked-in online and were to drop-off their bags were not spared the queues.
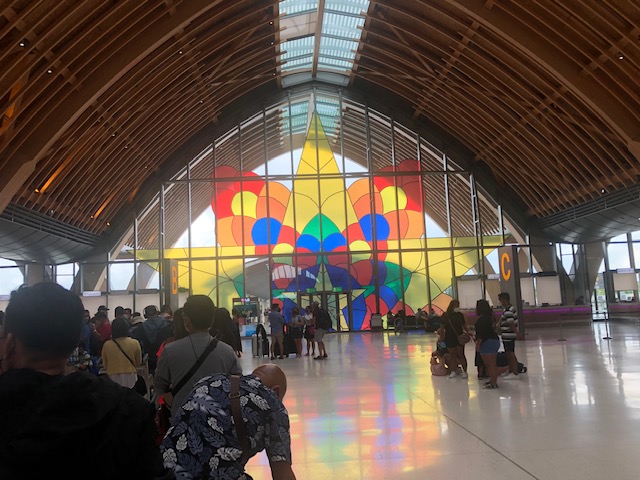 Stained glass windows featuring what appears to be a giant parol (Christmas lantern).
Stained glass windows featuring what appears to be a giant parol (Christmas lantern).
 A view of the other check-in counters at the spacious MCIA Terminal 2
A view of the other check-in counters at the spacious MCIA Terminal 2
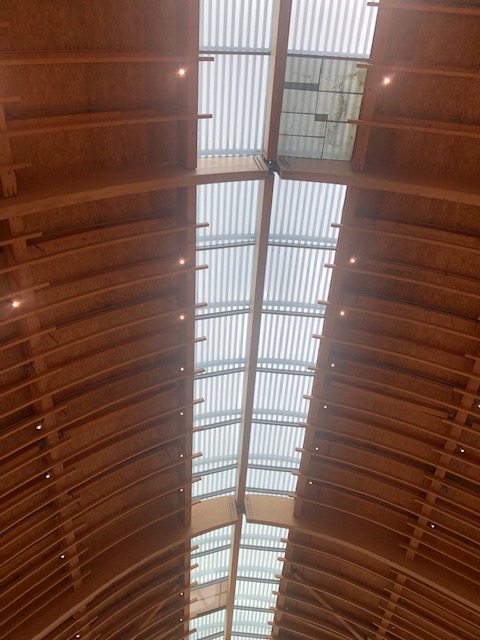 I took this photo of the ceiling to show the incorporation of natural lighting elements that allow for less power consumption for lighting particularly during daytime. This is one of the eco-friendly features of the building.
I took this photo of the ceiling to show the incorporation of natural lighting elements that allow for less power consumption for lighting particularly during daytime. This is one of the eco-friendly features of the building.
 Another view of the long queues for PAL after we finished checking-in.
Another view of the long queues for PAL after we finished checking-in.
 Airline service and information counters at the terminal – these are for Air Busan and Korean Air. An Air Busan plane figured in a crash recently when it overshot the runway upon landing at the MCIA in bad weather.
Airline service and information counters at the terminal – these are for Air Busan and Korean Air. An Air Busan plane figured in a crash recently when it overshot the runway upon landing at the MCIA in bad weather.
 Another view of the ceiling and roof
Another view of the ceiling and roof
 Guidance for passengers are posted at the check-in counters. These include info on items that are not allowed in the check in bags, what are prohibited and will be seized at the airport, and what are allowed only in check in bags. The scale readout is working and can be seen on the counter. Typical luggage limit for domestic passengers range from 20 to 25kg depending on the airline.
Guidance for passengers are posted at the check-in counters. These include info on items that are not allowed in the check in bags, what are prohibited and will be seized at the airport, and what are allowed only in check in bags. The scale readout is working and can be seen on the counter. Typical luggage limit for domestic passengers range from 20 to 25kg depending on the airline.
Part 2 is coming soon!
–
Traffic and air quality
Along one of my commuting routes, I couldn’t help but take a photo of what lied ahead as our vehicle was crawling along Marcos Highway in Antipolo. The following photo pretty much captures the relationship between transportation and the environment; the latter in terms of air quality and the former in the form of our congested roads.
 Smoggy Metro Manila in the horizon as vehicles are crawl along Marcos Highway towards Masinag Junction
Smoggy Metro Manila in the horizon as vehicles are crawl along Marcos Highway towards Masinag Junction
With traffic practically back or even worse than pre-pandemic levels, one cannot help but think about what could have been if government planned and executed during the time of the lockdowns in preparation for the eventual return to workplaces and schools by most people. The peak of the pandemic when total lockdowns were implemented was supposed to provide the opportunity to make the drastic changes required of transportation. You cannot find a better time for a reboot and yet here we are and again struggling with our daily commutes. We can just hope that other cities and municipalities will not go the way of Metro Manila.
–
On emergency vehicles, speeds and road widths
I recall an online discussion about how roads need to be wide to accommodate emergency vehicles such as fire trucks/engines, ambulances and police vehicles. There are also videos shared on social media about how, with wide roads, motorists could move their vehicles to the sides to give way to emergency vehicles. These are used to support the argument that we need wide roads and that speeding for emergency vehicles is justified because of their purpose. The following article attempts to make a counter-argument:
Lewis, M. (November 21, 2022) “Ambulances vs. Pedestrians,” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/blogs/119785-ambulances-vs-pedestrians [Last accessed: 11/24/2022]
To quote from the article:
“the “emergency response” argument in favor of wide streets only makes sense if the risk of death from a too-slow ambulance outweighs the risk of death from a speeding car.”
Certainly, the data on road crashes due to speeding should support the perception that there’s a higher risk of death from speeding vehicles compared to the risk of dying in relation to the emergency that’s supposedly being responded to. And in our country, perhaps this counter-argument is valid considering the “wang-wang” type of emergency vehicles moving about.
–
Commuting from/to Antipolo via the public transport terminal at Robinsons Antipolo
I was at the Robinsons Antipolo public transport terminal to take a P2P bus to Ortigas. I took a few photos before boarding the bus. The bus no longer terminates at Robinsons Galleria but instead goes to Greenhills. This is very convenient for people who need to go to Virra Mall or somewhere in its vicinity (e.g., Cardinal Santos Medical Center, LSGH, etc.).


Then there are the buses plying the Antipolo-Cubao route via Sumulong Highway-Marcos Highway-Aurora Boulevard. These are regular aircon buses (not P2P) operated by various companies including G-Liner, RRCG, Jayross, etc. Below are photos of Diamond Star buses loading passengers bound for Cubao.
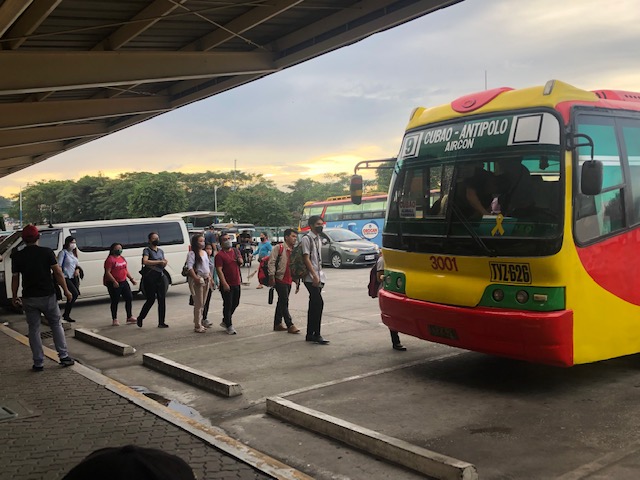


The lines can be very long depending on the time in the morning but I guess the assurance of a seat makes it worthwhile to go to the terminal rather than wait for the bus along its route. Passengers loads are practically back to pre-pandemic levels and with some jeepneys back, that means competition for the buses.
–
