Home » Highway Engineering
Category Archives: Highway Engineering
Safety roller barriers along Sumulong Highway
Last week, I observed that the DPWH is currently installing road safety barriers along a section of Sumulong Highway in Antipolo City. Previously, I posted about the same along the Antipolo-Teresa Road, which has treacherous zigzag sections. Here are photos of the ongoing installation work along Sumulong between Padi’s Point and the Oscar Lopez Center.
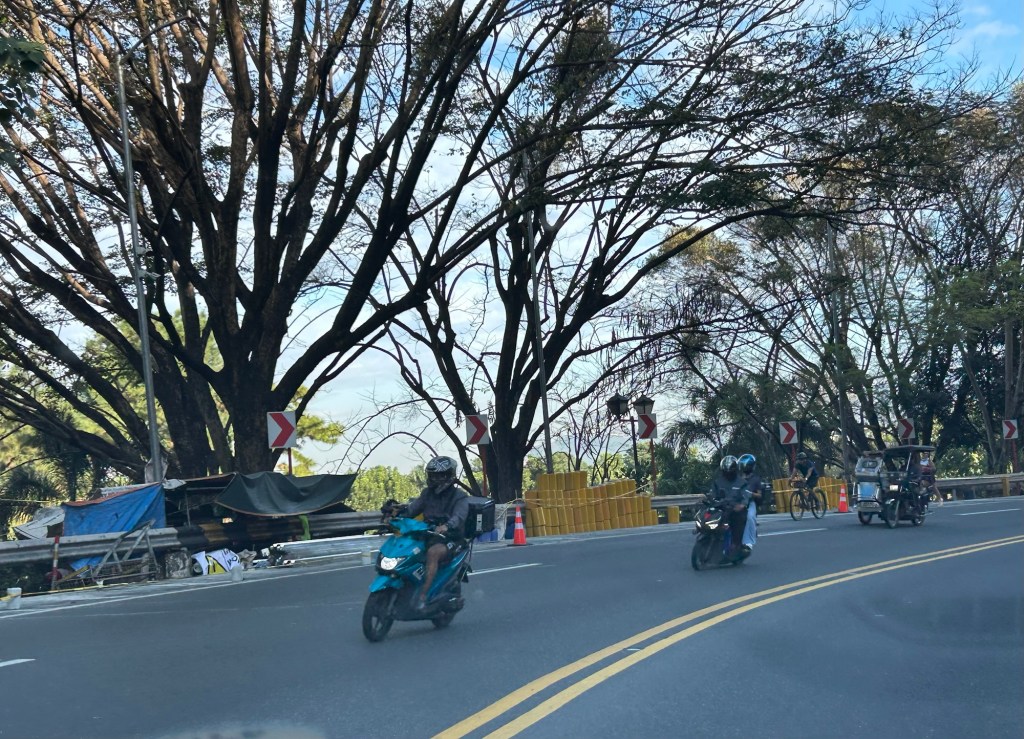
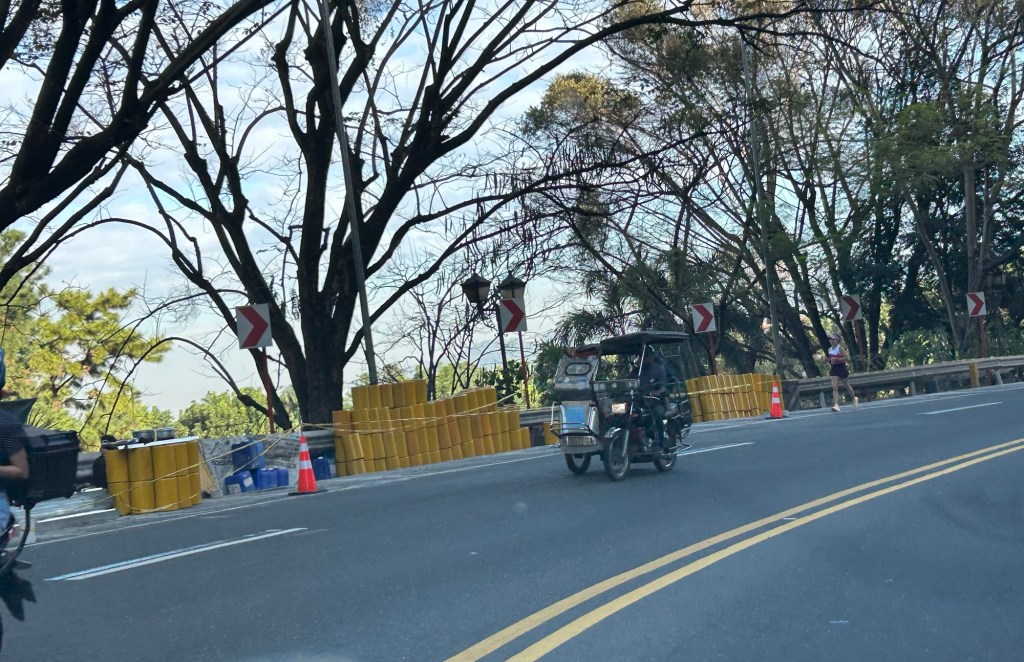
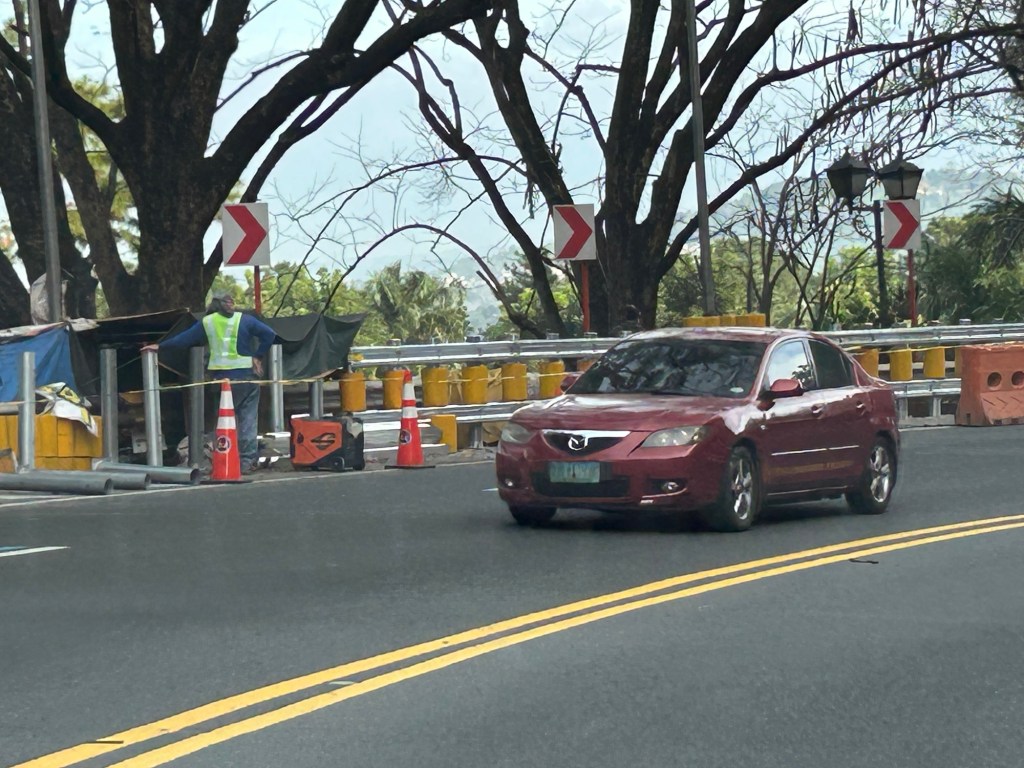
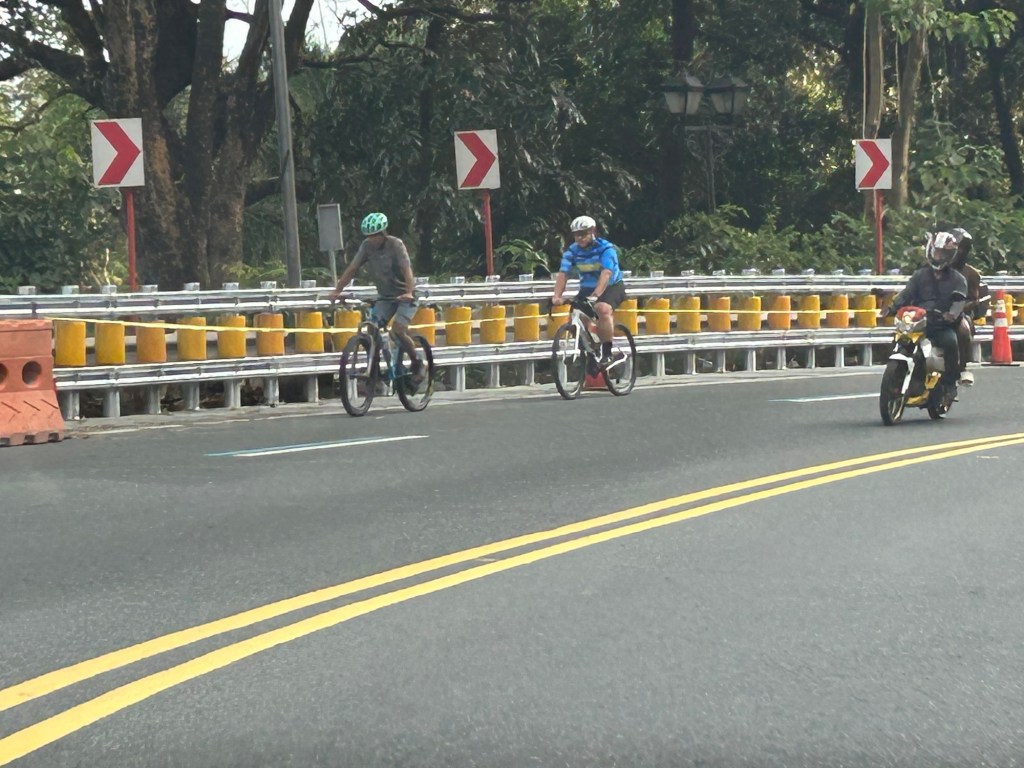




Here is a link to what these barriers are and how they help make roads safer for all users:
https://roadskyguardrail.com/what-is-a-safety-roller-barrier-a-comprehensive-guide
–
After getting engrossed with EDSA, is Marcos Highway next?
If you monitored the news articles and social media post over the past two decades, there seems to be an obsession for EDSA. Circumferential Road 4 is the busiest corridor in Metro Manila, stretching across several jurisdictions including Caloocan, Quezon City, Mandaluyong, Makati and Pasay City. Aside from the MMDA, national agencies like the DPWH and DOTr have been heavily involved in traffic schemes and transportation infrastructure development along the corridor. These include variants of the travel demand management (TDM) scheme commonly called number coding. Since the 1990s, there’s the Line 3 and several overpasses/flyovers and underpass that have been constructed along major intersections (e.g., EDSA-Shaw, EDSA-Ortigas, EDSA-Kamuning, EDSA-Quezon Avenue, etc.). Nowadays, people are more into the EDSA carousel and most recently the pavement rehabilitation for EDSA. It seems we failed to realize that EDSA is just one corridor. There are others that also demand attention including those in other parts of the country.
Recently, a “carmaggedon” along Marcos Highway was in the headlines or shall I say was trending in social media. There was a lot of excitement for what has been a recurring nightmare to those residing along the corridor. I recall something worse occurred more than 15 years ago (pre-Ondoy), before social media and influencers and digital creators. At the time, Line 2 terminated at Santolan Station. And even back then, the MMDA insisted on playing with their U-turn scheme. I don’t recall a more in-depth study that could have involved micro-simulation modeling being done for the corridor. And since then, populations and traffic have grown steadily and as I’ve written about previously, the extension of Line 2 to Masinag seems to have had little impact on traffic. And so here we are with the MMDA still insisting on tweaking their U-turn schemes and relying mainly on gut-feel instead of a more scientific approach that may actually lead to more sound solutions for the corridor.
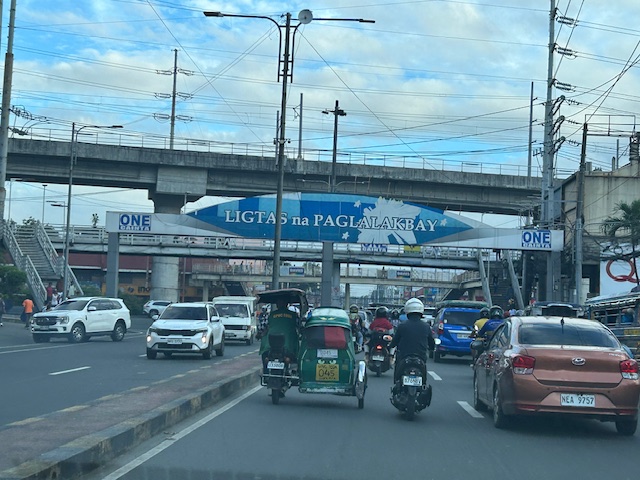 Approach to Marcos Highway from Felix Avenue – that’s the elevated Line 2 superstructure behind the Cainta arch.
Approach to Marcos Highway from Felix Avenue – that’s the elevated Line 2 superstructure behind the Cainta arch.
 Intersection of Marcos Highway, Felix Avenue and Gil Fernando Avenue – there’s a major foot bridge installed here so people can cross at the intersection, which used to be a signalized junction before the MMDA opted for U-turns for Marcos Highway sections under its jurisdiction.
Intersection of Marcos Highway, Felix Avenue and Gil Fernando Avenue – there’s a major foot bridge installed here so people can cross at the intersection, which used to be a signalized junction before the MMDA opted for U-turns for Marcos Highway sections under its jurisdiction.
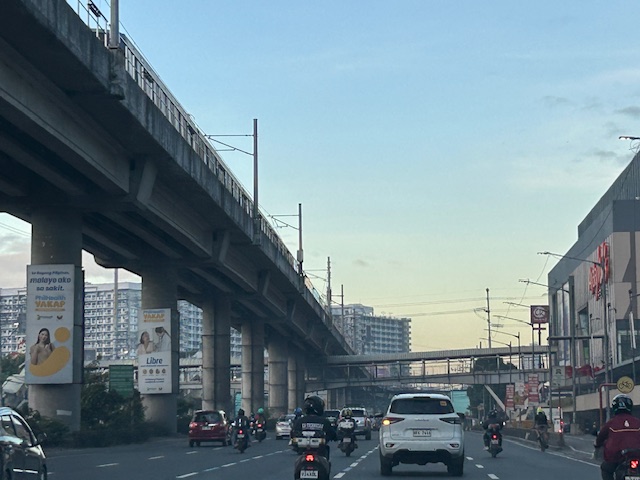 Marcos Highway section fronting the Ayala Feliz Mall – the MMDA has played with the location of the U-turn slots in the vicinity of the Marcos Highway-Amang Rodriguez-J.P. Rizal intersection as they tried to determine the “optimum” locations of these slots.
Marcos Highway section fronting the Ayala Feliz Mall – the MMDA has played with the location of the U-turn slots in the vicinity of the Marcos Highway-Amang Rodriguez-J.P. Rizal intersection as they tried to determine the “optimum” locations of these slots.
Of course, there is also the case of Commonwealth Avenue. How many carmaggedons have occurred along that corridor? Isn’t it an everyday thing there? And there’s also Ortigas Avenue Extension and many other roads and streets where congestion seems to have been accepted as the norm. How do we make travel easier for most people? How do we improve commutes given the constraints and realities concerning behavior and choices?
–
Traffic calming devices in the vicinity of schools – speed tables
Traffic calming devices are an effective means to reduce speeds especially where there are many pedestrians crossing the streets. These are usually applied near schools where there are significant numbers of pedestrians, particularly schoolchildren. Following are examples of raised crossings or speed tables located at the approaches and exits of an intersection in Naga City. These are located at the intersection of J. Hernandez Avenue and P. Burgos Street. Burgos leads straight to the main gate of the University of Nueva Caceres. However, there is no raised crossing for Burgos. There are only those for both legs of Hernandez.
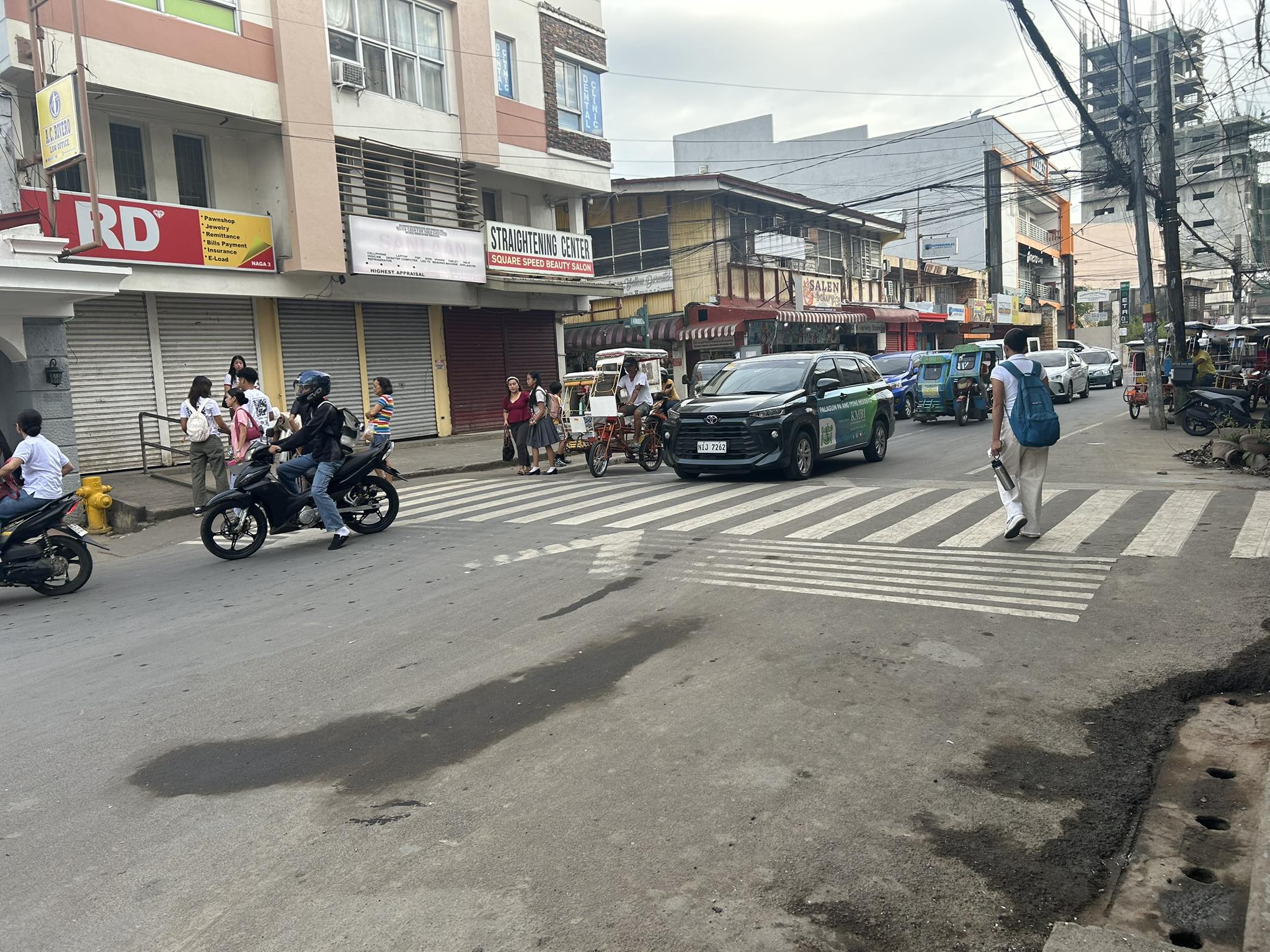 Speed table along north approach of J. Hernandez Avenue
Speed table along north approach of J. Hernandez Avenue
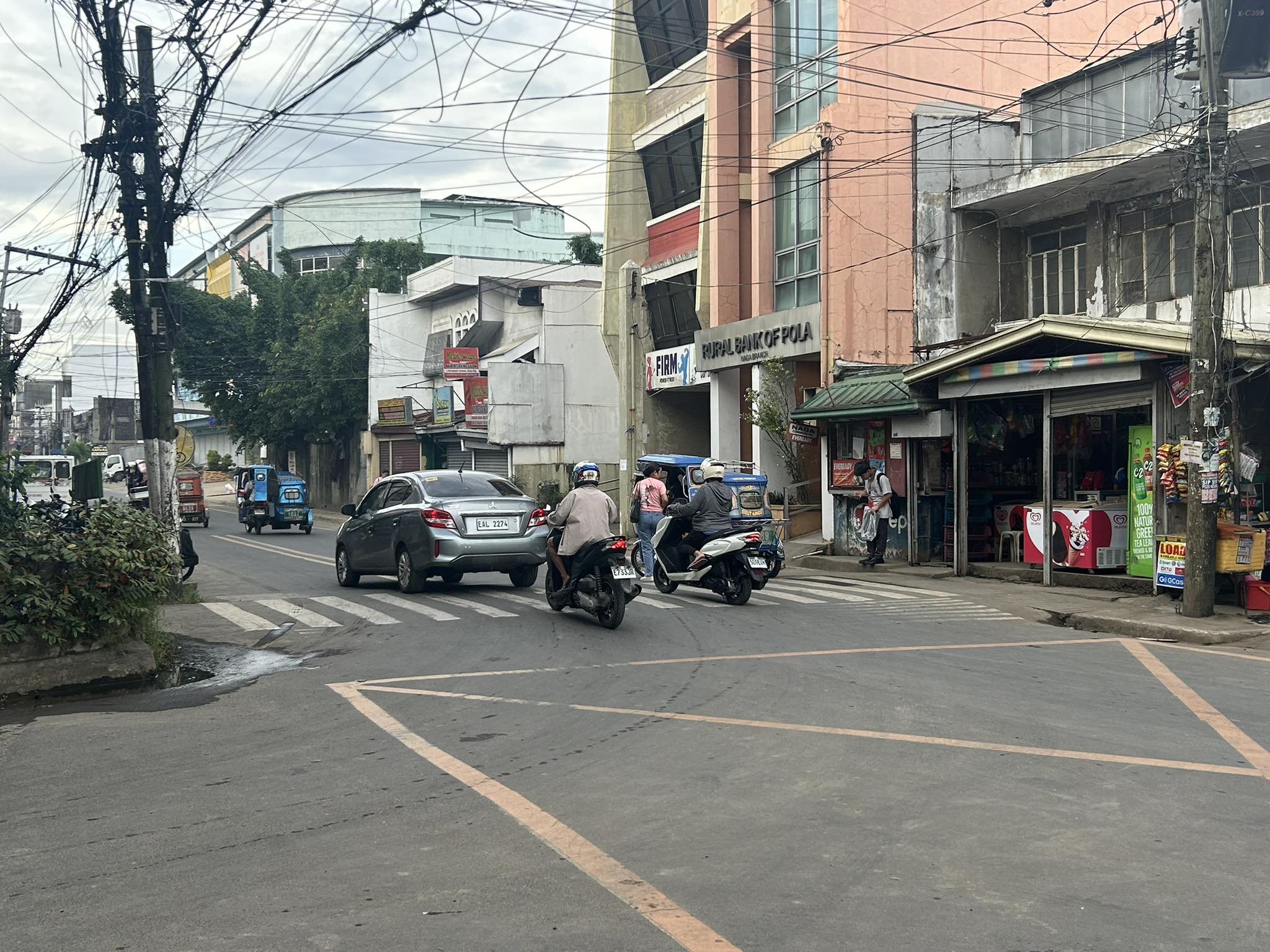 On the other side, there is another raised crossing along J. Hernandez Avenue.
On the other side, there is another raised crossing along J. Hernandez Avenue.
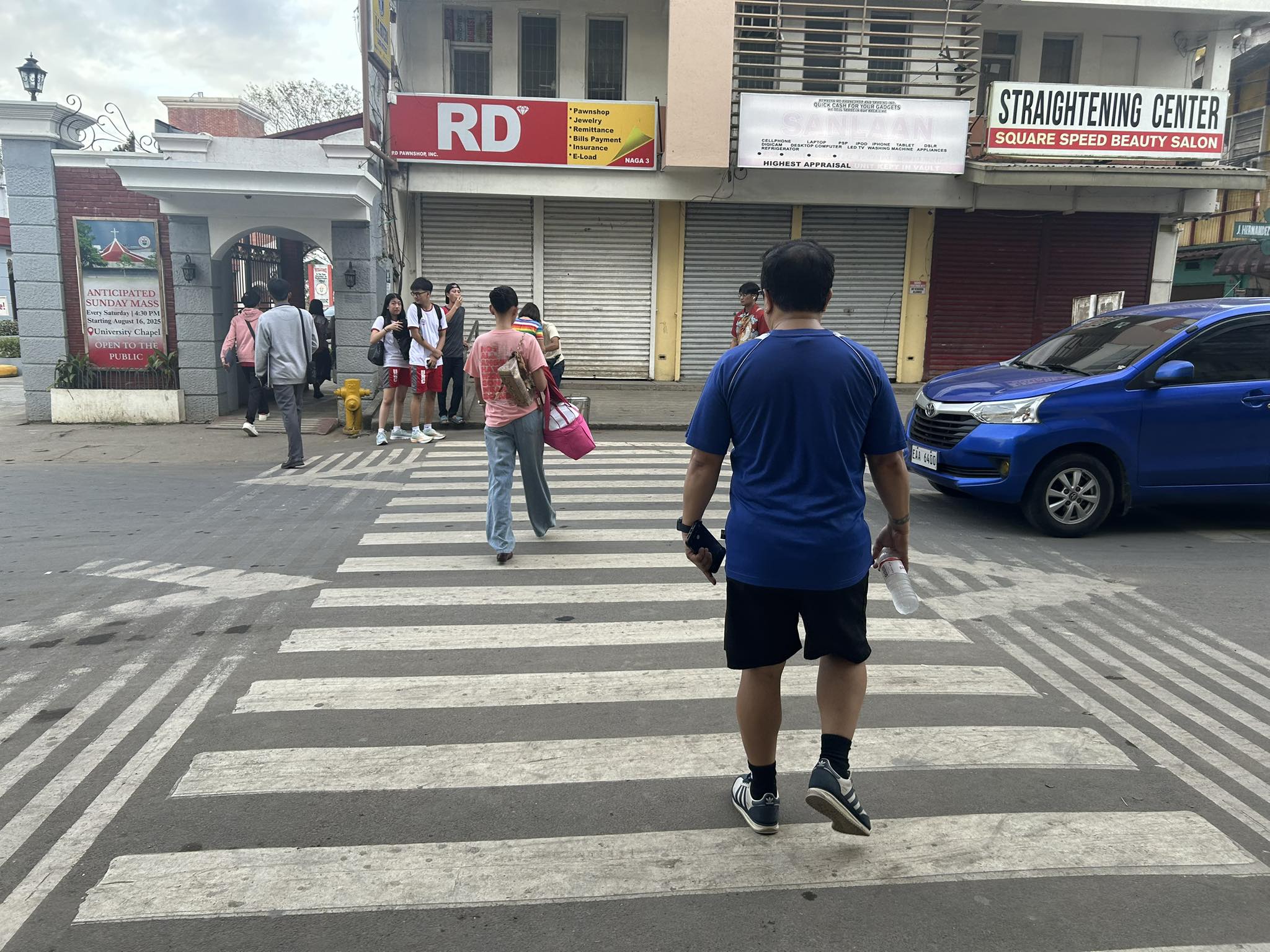 POV of a pedestrian crossing at the speed table towards the UNC main gate (to the left in the photo).
POV of a pedestrian crossing at the speed table towards the UNC main gate (to the left in the photo).
There is a need to have these traffic calming devices in other locations across the city and particularly near schools where crossings are located and vehicle speeds need to be reduced. There should be no exceptions for the application of traffic calming. That includes national roads along which certain agencies like the DPWH like to maintain higher speeds despite the obvious risks posed on pedestrians. Many schools are located along national highways and raised crossings can be designed to reduce speeds while offering safe crossings to schoolchildren. We just have to change mindsets pertaining to safety and priorities.
–
On how delivery culture is influencing policy and urban design
While discussing on-street parking policies and schemes with Naga City LGU officials, one comment was on providing parking space for delivery riders. Truly, delivery riders have become a significant consideration especially where they have no parking spaces to wait or sort their items. The following articles expounds on how the rise of delivery culture is influencing policy and urban design:
Franco, A. (November 14, 2025) “From edge to epicenter: How the curb became a key piece in modern cities,” Public Square, https://www.cnu.org/publicsquare/2025/11/05/edge-epicenter [Last accessed: 11/14/2025]
To quote from the article:
“Urban designers need to recognize that while our streets were once built exclusively for car movement and storage, they are inherently adaptable. The opportunity now is to make these spaces more equitable, accessible, and efficient for everyone, not just car owners with parking privileges. After all, the street and the curb are public spaces and should serve the diverse needs of all citizens.”
Complicated intersections in Rizal – Tikling Junction
There are several major intersections in Rizal Province. Among them are 3 junctions in Cainta, Taytay and Antipolo – Cainta Junction (Ortigas Ave Ext.-Felix Ave), Masinag Junction (Marcos Highway-Sumulong Highway), and Tikling or Kaytikling Junction. The first two are signalized intersections. The last one is supposed to be a roundabout. All three are problematic in various ways and have been associated with congestion along the major roads intersecting at these junctions.
Tikling is quite interesting as traffic seems to have worsened after it was set up as a roundabout. Taytay enforcers have been deployed here but they seem to contribute more to worsening congestion rather than easing it. Motorists familiar with the area will tell you that traffic is better when there are no enforcers. Unfortunately, not all motorists here are from the area or are familiar with the rules for navigating or positioning at a roundabout. And so the intersection is often constricted with vehicles whose drivers and riders don’t practice courtesy.


Perhaps a combination of geometric improvements and more clever enforcement/management can improve intersection performance?
–
Pothole season
The heavy rains the past days have taken a toll on many roads. Special mention here would be city roads such as main arterials where traffic flow is affected by the pavement conditions. Here are a couple of photos of potholes along Katipunan Avenue.


The photos also reveal that cement concrete slabs are actually under the asphalt concrete. This means asphalt concrete was used more as an overlay to protect the cement concrete slab rather than as the main structural component that will carry the traffic loads. The pavement slabs may not necessarily be compromised but the hammering action of tires/wheels as they hit the potholes will definitely lead to more damage. The water, of course, is worrisome because once they seep or penetrate the cracks and interfaces between the slabs, they may compromise the layers beneath the slab. This will weaken the foundation of the pavement and lead to more critical damage. The challenge is how to repair these potholes when we are still experiencing heavy rains. Now that’s something the DPWH needs to figure out, learn and apply rather than the usual patch up work that results in mounds of asphalt replacing the potholes.
–
Bollards along Marcos Highway
I noticed that there are new bollards installed along Marcos Highway and particularly along the curbs at either side of the road. These were installed only recently, perhaps last month, nut I only got a few photos the other day. Its not safe to take photos while one is driving so I asked the wife to take a few ones that I could use here and perhaps also in some of the lessons I teach.
 These bollards are installed along the curb where a couple of fatal crashes occurred in the past months.
These bollards are installed along the curb where a couple of fatal crashes occurred in the past months.
The bollards are probably there to help improve road safety. They are reflectorized to you can’t miss them at night. Immediately behind them though are concrete barriers so hitting these will definitely damage the vehicle with a possibility of serious injuries to the vehicle occupants if not fatalities. Could there be a safer design intervention here? Perhaps that curbside lane can be converted into a protected bicycle lane. The barrier and the bike lane itself will be a buffer zone between motor vehicle traffic and active transport including pedestrians.
–
On understanding road diets
I’ve written and shared articles on road diets and complete streets before. Here is another article share on road diets
Johnson, R. (April 21, 2025) “Explainer: What is a Road Diet – And Why Should Cities Embrace It?,” Momentum Magazine, https://momentummag.com/explainer-what-is-a-road-diet-and-why-should-cities-embrace-it/ [Last accessed: 22/04/2025]
To quote from the article:
“The road diet isn’t about punishing drivers. It’s about creating streets that work better for everyone—from the parent pushing a stroller to the teenager biking to school, the delivery driver navigating a tight urban corridor, or the senior walking to the store.
As our cities continue to evolve, road diets offer a cost-effective, data-backed, and scalable way to make them safer, cleaner, and more livable. It’s not just about losing a lane—it’s about gaining a better future for urban mobility.”
Indeed, the first thing that usually comes to mind of motorists whenever road diets and complete streets are mentioned is that the road space (and consequently capacity) will be reduced. This reduction of capacity is actually from the perspective of the motor vehicle rather than the number of people traveling along a road as well as improving road safety for all. The article is spot on in its discussion on the resistance to road diets (and complete streets). Of course, context is very important here and it is important to identify which roads can be transformed for the transformation to be most effective.
–
On C-6 and the proposal for another expressway, Part 2
The recent announcement and launch of the Southeast Metro Manila Expressway (SEMME) included this map showing the (very) rough alignment for the proposed tollway. The map also shows the proposed locations of interchanges including one in Tikling and another in Masinag. There is also another in Tumana. From the looks of this, the SEMME will be a skyway or elevated expressway/tollway.
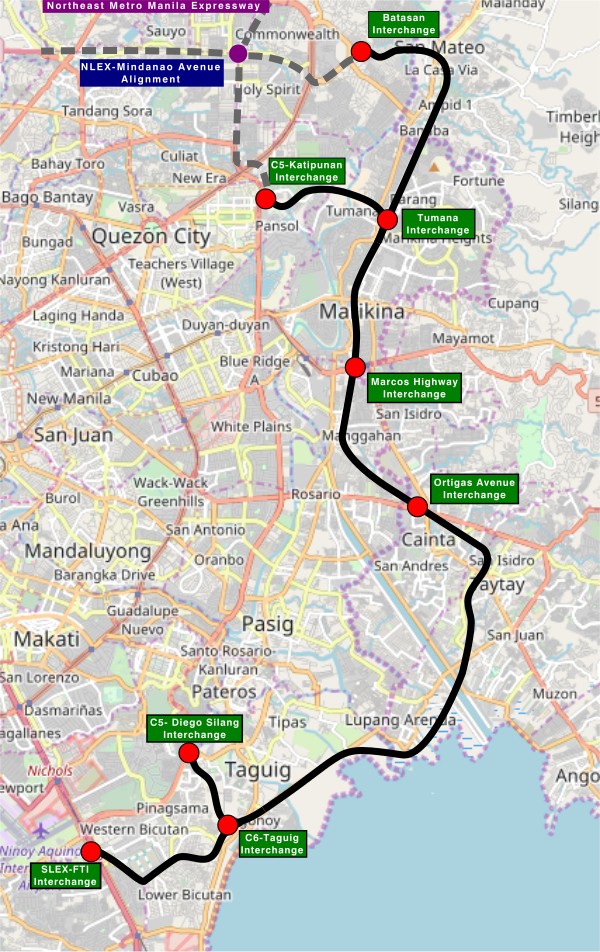
My first impression is that this elevated tollway will pass through predominantly residential areas with columns rising from private subdivisions. It doesn’t help that the topography also means the columns will be built along hilly or mountainous terrain, thereby making construction more challenging than the elevated tollways in Metro Manila.
Do we really need another circumferential road and particularly another tollway? I think that is a very important question that not only needs to be asked but also answered the right way. I, for my part, don’t believe we need another tollway, elevated or not, as this will not solve the so-called traffic problem. In fact, it creates more problems than what is supposed to be solved with the induced traffic this will generate and its promotion of car-centricity. For the price and effort of such an infrastructure, you will get more bang for your buck with a mass transit line or lines. Road congestion can only be solved by constructing the public transport system we needed decades ago.
–
Another look at the Candaba viaduct’s new lanes
I recently wrote about the new lanes along the Candaba viaduct and my thoughts about them being used as variable lanes (i.e., more lanes assigned along the peak or heavier traffic direction). Only this January 2, I observed that the lanes were being used instead for the southbound traffic as the older southbound viaduct appeared to be closed to traffic. Perhaps that side is up for rehabilitation or maintenance work?
 The new lanes between the two viaduct structures are now in use.
The new lanes between the two viaduct structures are now in use.
 These are assigned to southbound traffic while the original lanes appear to be closed off.
These are assigned to southbound traffic while the original lanes appear to be closed off.
–
