Home » Pedestrian (Page 3)
Category Archives: Pedestrian
Bike lane master plan for Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao
The Department of Transportation (DOTr) with support from the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) yesterday formally launched the Bike Lane Master Plan for Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao. Yesterday’s event was actually the third and last leg of presentations, which were also made in Cebu and Davao. Here are a few photos I got from the DOTr Facebook page (these are public):
 Printed copies of the master plan were distributed to attendees (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
Printed copies of the master plan were distributed to attendees (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
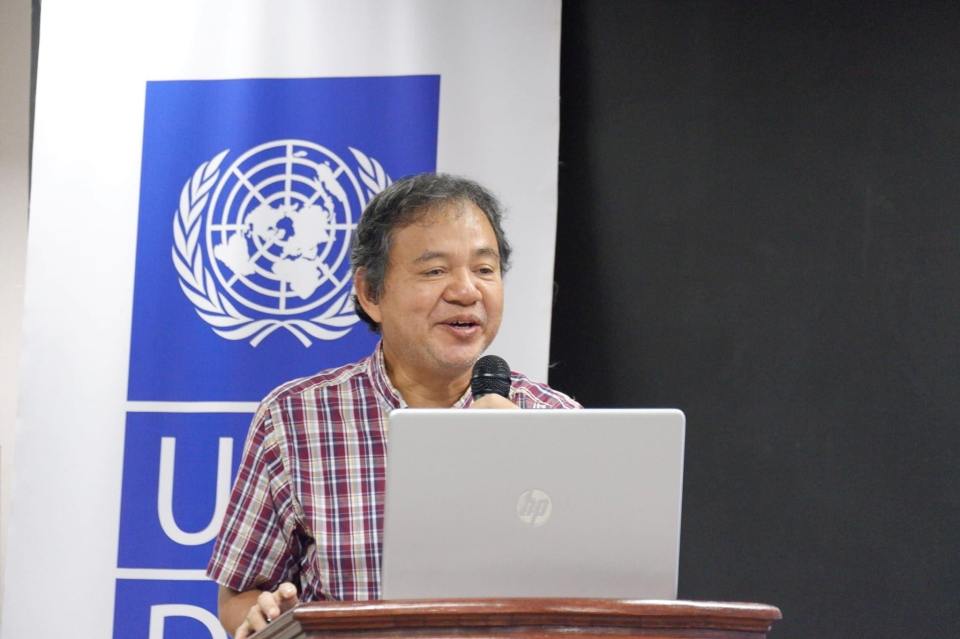 Dr. Ricardo Sigua of the National Center for Transportation Studies presented the highlights or key features of the master plan. The UNDP engaged NCTS to conduct the master planning project for DOTr. (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
Dr. Ricardo Sigua of the National Center for Transportation Studies presented the highlights or key features of the master plan. The UNDP engaged NCTS to conduct the master planning project for DOTr. (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
 Photo op with participants from the MMDA (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
Photo op with participants from the MMDA (Photo: DOTr Facebook page)
While the master plan is most welcome as the country continues to build infrastructure for active transport (mainly walking and cycling), the launch is actually one year late. The project was actually completed last year and though most of the recommendations have yet to be carried out, many items including the inventories are already dated. These master plans though should not be static documents but dynamic in these sense that it would have to be updated regularly. For one, updates would provide the opportunity to reinforce or improve certain aspects of the plan. Updates also provide an opportunity to check whether progress is being made on the targets set in the plan. Also, since the master plan is for three metropolitan areas perhaps it can be part of the foundation for a nationwide plan. However, many plans fail if there is not support or scarce resources allocated for the implementation. Thus, there is a need for resources or allotments especially coming from government to support the realization of the plan.
–
Article share: What’s Incomplete About Complete Streets?
The concept of road diets circulated in Metro Manila more than a decade ago. I recall the Metro Manila Development Authority (MMDA) picked up the concept and attempted to apply it in some parts of Metro Manila. Since there are no evidence of that endeavor surviving now, then we can assume that it was a failure. There is no wonder there as I also recall the effort to be half-hearted and more to get media mileage (cheap talk or lip service) out of it. Road diets eventually evolved into the complete streets (though the literature now will state road diets as part of complete streets). That experience and similar initiatives of varying success (or failure) rates are not unique to the Metro Manila but is actually happening elsewhere including cities in countries where the complete streets have been applied more comprehensively and yet somehow found to be lacking or not as effective a solution as expected. I am sharing an article here that discusses what seems to be lacking or ‘incomplete’ as it is referred to.
Source: What’s Incomplete About Complete Streets?
Quoting from the article:
“What’s missing? First of all, even the best Complete Streets policy can’t solve the problem of fiscal scarcity. Even in a city committed to Complete Streets, street redesign must fight for public dollars with other worthy goals such as education and public safety. As a result, Indianapolis’s improvements are a drop in the bucket. The city maintains 3,400 miles of streets and roads, so its 100 miles of bike lanes affect only 3 percent of the city. Similarly, 2,000 miles of the city’s roads still lack sidewalks.
Second, the quantitative benchmarks seem to focus on sidewalks and bike lanes (Sec. 431-806), and the policy doesn’t mention traffic calming or similar policies. So if the city had a six-lane road with traffic going 60 miles per hour, the Complete Streets policy would not affect that road except to the extent necessary to build a sidewalk or a bike lane.** Thus, even the best Complete Streets policies don’t really address some of the most dangerous features of American street design.”
—
Cool Walkability Planning
I am sharing this article about planning and design for more walkable streets. The term ‘cool’ in the article refers to temperatures as people are less likely to walk if it is too hot to do so.
From the article:
“Improving walkability (including variants such as wheelchairs, hand carts, low-speed scooters) can provide significant benefits to people, businesses and communities, particularly in dense urban areas where land values are high and vehicle travel is costly. However, walking can be uncomfortable and unhealthy in hot climate cities, particularly those that often experience extreme temperatures (over 40° Celsius, 105° Fahrenheit). These conditions make walking unattractive and infeasible during many days…
A well-planned networks of shadeways (shaded sidewalks) and pedways (enclosed, climate-controlled walkways) incorporated into a compact urban village can provide convenient, comfortable and efficient non-auto access during extreme heat. They can create multimodal communities where residents, workers and visitors rely more on walking and public transit, reduce vehicle use, save on vehicle costs, and require less expensive road and parking infrastructure…
The main obstacle to comprehensive pedway development is the well-entrenched biases that favor motorized travel and undervalue non-motorized modes in transportation planning and investment. Transportation agencies have tools for planning and evaluating roadway improvements, and funding to implement them, but lack comparable tools and funding for walkability improvements such as shadeways and pedways, even if they are more cost effective and beneficial than roadway projects.”
Source: Cool Walkability Planning
Short cuts in Zamboanga City
Our capacity building workshop in Zamboanga involved not just lectures and workshops but some practical exercises to demonstrate the surveys needed for road safety assessment of schools. Fortunately, there was a nearby school to our workshop venue and we only needed to walk to the school where participants could set up at certain locations to simulate data collection. Since a couple of teachers participating in the workshop were from the area and the nearby school, they led us to a short cut to get to their school. The route included a walk along a paved path along one of Zamboanga City’s streams.

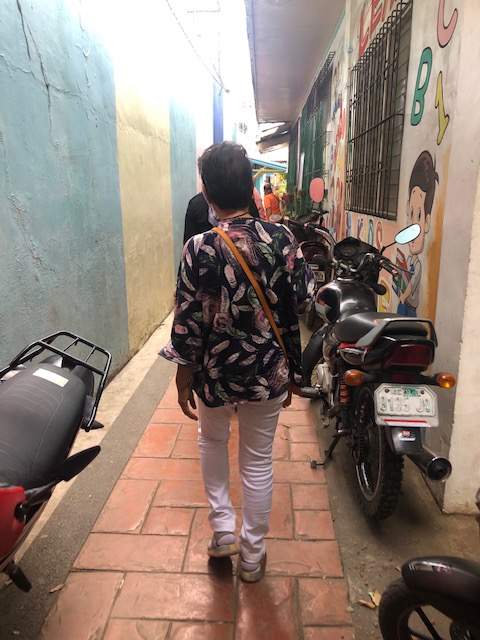



The area had a smell (stink?) to it. That was likely because it was the dry season and the heat meant the dirty water from the stream evaporated and generated the smell. There were even large rats that we saw swimming in the waters! Our guides told us that it was better during the wet season as the water flowed faster and was cleaner due to the rains and runoff. They also related about them bathing in the stream during their childhood days (I assume this was more than 30 years ago.) and before the structures above were constructed. The pathways were clean and secure though and there were others like these that we thought were good examples of pedestrian infrastructure that promote safety as well as encourage walking as a preferred mode of transport especially for short trips.
–
Article share: on pedestrian facilities and climate change
Here is an article that articulates the importance of walking and pedestrian facilities in sustainability and ultimately fighting climate change. It argues that if we had the infrastructure and facilities to make it easier for people to walk, they will and are likely to walk rather than use their cars. This is not limited to short trips as walking can be in combination with public transportation, making it an integral part of trips where public transportation covers the main commute and walking is the proverbial last mile travel.
To quote from the article:
“Walking, biking, and transit need to be prioritized, and treated as legitimate forms of transportation. This means stepping up efforts to collect data on sidewalks the way we do for roads, investing in complete walking networks before engaging in expensive new road projects and making sidewalk construction and maintenance a municipal responsibility rather than an individual one.”
Push and Pull: The Link Between Walkability and Affordability
Here is a quick share of an article about the link between walkability and affordable housing.
To quote:
“While early pandemic pundits predicted the ‘death’ of urban areas, recent trends show that people—perhaps more than ever—value the benefits of compact development and easily accessible amenities and services. But “Demand drives up costs and can reduce low- and moderate-income households’ opportunity to live in highly walkable areas,” the report warns.”
Source: Push and Pull: The Link Between Walkability and Affordability
Some people seem to be baffled why people choose to purchase homes and reside in the suburbs or away from the city centers. It is actually simpler than what many tend to overthink and attribute purely to the condition of our transportation system. It takes two (or more apparently) to tango and housing affordability is critical for the Philippines’ case.
–
On the need to change mindsets about bike lanes
Public acceptance of bike lanes has grown during the pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, there were few supporters especially among local government units and national agencies that seem to be comfortable with the status quo. Few like Iloilo and Marikina had any bike facilities worth mentioning. The pandemic was supposed to change that and it did for many. However, the acceptance and the gains seem to be eroding as we return to face-to-face activities and the ‘old’ normal situation.
I’m sharing below an article on the need to change mindsets about bike lanes and cycling in general:
Thompson, C. (January 24, 2023) “The Battle Over Bike Lanes Needs a Mindset Shift,” Wired, https://www.wired.com/story/the-battle-over-bike-lanes-needs-a-mindset-shift/ [Last accessed: 1/27/2023]
To quote from the article:
“Maybe bike lanes will always be fraught, until enough of the public is finally in a true lather about climate change—and it seems reckless to not have them.
Crises, after all, have a way of opening people’s eyes to possibilities. During Covid, restaurants and cafés lost so much business that cities nationwide began allowing them to build curbside seating areas where people could sit, safely, in the open air. It greatly reduced parking—but because, well, crisis, shop owners didn’t see any way around it. Patrons loved the outdoor seating so much that cities are making it permanent: A New York City study of several streets closed during Covid found storeowners making more than before, and diners digging the al fresco lifestyle. If data won’t change minds, customers might.”
There are two opposing sides on this matter. On one side are advocates who naturally will push for bike lanes and will promote them as The solution (emphasis mine) rather than one of a cocktail to address the transport mess we are in. On the other side are conservative, status quo types (or car-lovers as bike advocates will call them) who believe cars should have the roads to themselves. Unfortunately, many in government and particularly in transport agencies are with the latter. Perhaps they should be the first ones that need to be converted to favor active transport?
–
Why do we keep widening roads?
I’m just going to share this article here. The article from The NY Times asks a question that has been bugging planners and engineers, particularly those who are in government and perhaps under the agencies like the DPWH, DOTr and NEDA. This also applies to planners, engineers and those from other disciplines involved in transportation infrastructure development and particularly roads or highways.
–
Examples of legislative actions in support of active transport
While the Philippine government and various local government units seem to be reneging on their commitments to support active transport, other countries have been building on their gains during the pandemic. Here are examples of legislations in New York State that will support active transport through funding of complete streets projects and institutional arrangements for representation of transit dependent individual:
The article is about two legislations:
Legislation (S.3897/A.8936-A) Provides Funding for “Complete Streets” Projects Inclusive of a Holistic Approach to Street Design
Legislation (S.3959-B/A.7822-C) Adds Board Seats to NFTA, RGRTA, CDTA, and Central New York Regional Airport Authority Dedicated to a Transit Dependent Individual
We hope to see something like these at least at the local level. Perhaps if LGUs are able to legislate and implement these, there will be more good practice examples that will compel national government to support active transport development. The latter is actually ironic considering that many plans are supposed to spell out the national government’s commitment to active transport. There are still live memorandum orders and department orders supporting and promoting active transport. Are these also being waylaid? That will be tragic for transportation if we didn’t learn or gain anything from the experiences during this pandemic.
–
On the future of bike lanes in Metro Manila and other cities and municipalities in the Philippines
My friends and I were talking about the current buzz about the bike lanes including statements made by certain personalities (influencers, advocates, government officials, etc.) about biking and bike lanes. There were many recent pronouncements of motorcycles being allowed to use bike lanes or the outright removal of bike lanes. We all agreed this was backward and the way forward is to build on the current network and facilities. What we have in our cities and municipalities are not perfect and far from ideal but they are a start and perhaps the foundation for a bikeway network that can eventually make a dent on the car-centric transportation we have.
I share below the strategies, actions and targets for bicycle facilities, programs and projects from the Network Planning for the Establishment of Bike Lanes in Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao that was completed middle of 2022. The project is DOTr’s with support from the UNDP. The table is from the Final Report of the project.




A Happy Christmas to all!
–
