Home » Public Transport (Page 14)
Category Archives: Public Transport
On priority lanes for public transport
I am currently part of an International Research Group (IRG) involved in studies on bus priority. Yesterday, we had a meeting where one professor mentioned the importance of being able to clearly explain the advantages of having priority lanes for buses in order to improve their performance (i.e., number of passengers transported and improved travel times). There was a lively discussion about how the perception is for bike lanes while transit lanes have also been implemented for a long time now though with mixed results.
There are very familiar arguments vs. taking lanes away from cars or private motor vehicles and allocating them for exclusive use of public transport and bicycles. It may sound cliche but ‘moving people and not just cars’ is perhaps the simplest argument for priority lanes.
 EDSA carousel buses lining up towards a station
EDSA carousel buses lining up towards a station
 Bike lane along Katipunan Avenue – is this a temporary thing? a fad because traffic is really not back to the old normal? Katipunan is infamous for being congested with cars generated by major trip generators in the area such as schools/universities and commercial establishments.
Bike lane along Katipunan Avenue – is this a temporary thing? a fad because traffic is really not back to the old normal? Katipunan is infamous for being congested with cars generated by major trip generators in the area such as schools/universities and commercial establishments.
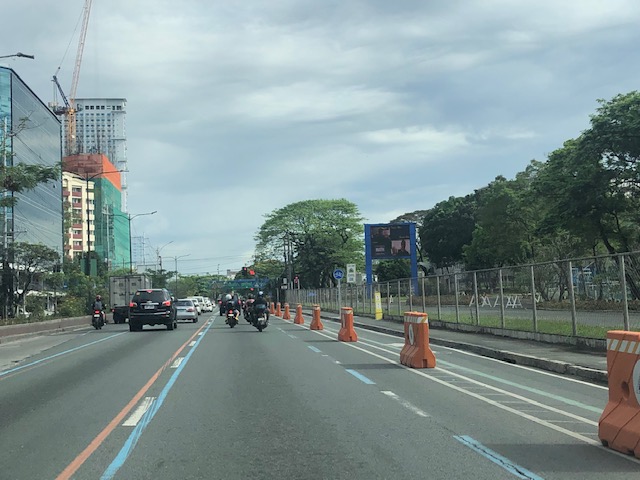
 The bike lane along Commonwealth Avenue proves there’s just too much space for private motor vehicles. And with the Line 7 in the horizon, perhaps more lanes can be taken and made exclusive to road public transport. [Photo credit: Cenon Esguerra]
The bike lane along Commonwealth Avenue proves there’s just too much space for private motor vehicles. And with the Line 7 in the horizon, perhaps more lanes can be taken and made exclusive to road public transport. [Photo credit: Cenon Esguerra]
–
On defining the 15-minute city
I have shared articles and briefly written about the concept of the 15-minute city on this blog. Here is another discussing how a 15-minute city is defined:
(February 8, 2021) “Defining the 15-minute city,” Public Square, https://www.cnu.org/publicsquare/2021/02/08/defining-15-minute-city [Last accessed: 8/10/2021]
Here is an image from the article:
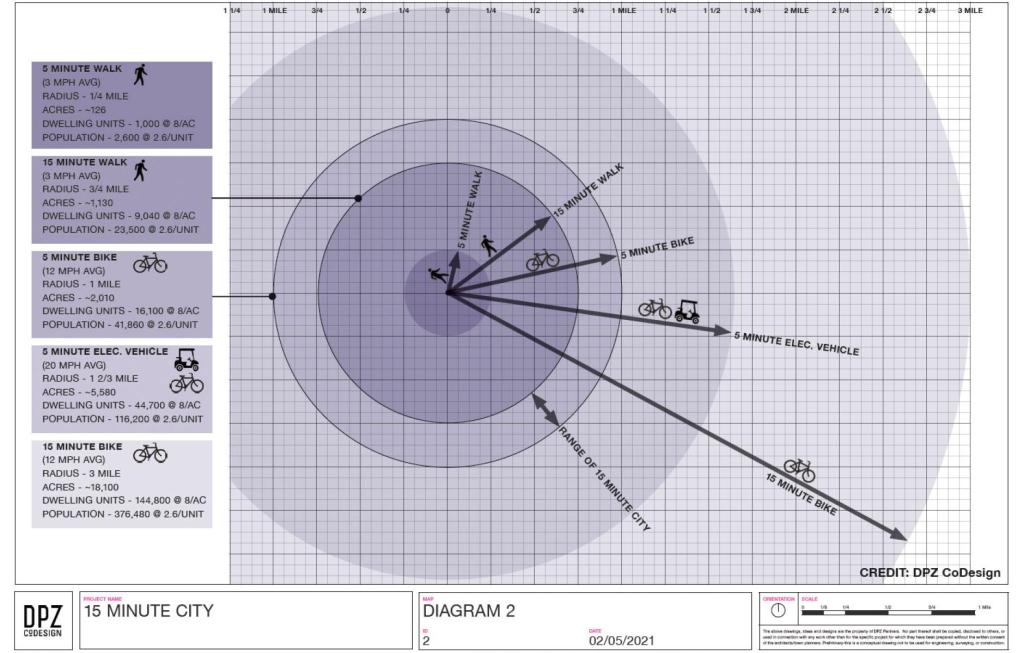
Again, it is important to contextualize these concepts. I share these as references and topics for discussion. Of course, I have my own opinions about this and I have written about those in previous posts. I guess in the Philippine context, we can include the pedicab or non-motorized three-wheelers in the discussion. These are also very popular modes in many cities and municipalities despite their being also prohibited along national roads like their motorized counterparts. It would be nice to have more visuals in the form of maps that show travel times for essential destinations or places like hospitals, markets, grocery stores, workplaces and, of course, homes. I assume there is at least someone, somewhere who perhaps have made multi-layer maps of this sort and attempted to related them along the lines of this concept of a 15-minute city (or perhaps the even older “compact cities”).
–
On the BRT gaining popularity
Bus rapid transit or BRT has been around at least since the 1970s when the first ‘real’ BRT systems went into operation in Curitiba, Brazil. Here’s an article presenting the current state of deployment of these systems in the US:
Duncan, I. (July 23, 2021) “Cities are turning to supercharged bus routes to more quickly and cheaply expand transit services,” The Washington Post, https://www.washingtonpost.com/transportation/2021/07/23/bus-routes-public-transit-brt/
“There are indications that BRT lines can promote some of the density long associated with rail routes. A new analysis of job and residential growth by researchers at the University of Arizona examined areas around BRT stations in 11 cities between 2013 and 2019. In each case, they found areas close to the stations accounted for a significant share of regional growth.”
The Philippines should have had its first BRT line more than a decade ago if the government had been decisive about it. The first opportunity was under the administration of Macapagal-Arroyo when it was first conceptualized for Cebu City under a UNDP project and picked up by the WB for implementation.* The next opportunity came under the Aquino administration when the Cebu BRT could have been one of those low-hanging fruits for public mass transportation. Now, the same project is nowhere near completion as the Duterte administration has less than a year before it bows out. Meanwhile, there are proposed BRT’s in Metro Manila and Davao that have yet to see the proverbial light of day. The EDSA carousel is supposed to morph into a BRT but has not become so and requires more tweaking for it to be one.
*[Note: The BRT that was supposedly implemented by the MMDA under its then Chair Bayani Fernando was not a BRT or even a BRT light. It is not even at the scale of the current EDSA carousel.]
Tinkering with decentralization of public transportation planning, franchising and regulations
I recall an informal discussion my colleagues and I had about the then Department of Transportation and Communications (DOTC) more than a decade ago. We were comparing the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH)’s and DOTC’s structures. DPWH has regional offices but also District Engineering Offices (DEO). These DEOs were practically mini me’s of the DPWH with the District Engineer calling the shots. Under him were a Design Engineer, Planning Engineer, Maintenance Engineer, etc. who were the equivalent at that level of the Bureaus. DOTC didn’t have the equivalent even though there were Land Transportation Office (LTO) and Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board (LTFRB) regional offices. So if there were regional development council (RDC) meetings, the DOTC’s representatives are usually from the regional offices of LTO and LTFRB plus other offices of agencies under DOTC – Maritime Industry Authority (MARINA), Air Transportation Office (ATO now CAAP) and the Philippine Ports Authority (PPA).
I mention these because perhaps one vision for the future is to have something like Metropolitan, City or Municipal Transit Authorities similar to those you’ll find in other countries. And these should have the capacities for route planning and assessment that are currently centralized in DOTr (i.e., Road Transport Division). But perhaps these transit authorities should not only have road based public transport under them but also rail, too. This is especially applicable to metros like MM, the loosely defined Metro Cebu and Metro Davao and other HUCs that maybe ripe for some form of urban rail transport. In some cases, I would even dare include maritime transport as well since modes like the Pasig River Ferry should also be included.
This idea of decentralization is something worth considering as local government units build capacity and capability for public transportation planning, operations and management. Some are already capable though mainly concern themselves with tricycles and pedicabs. These two modes are not under the LTFRB but are arguable the most in number around the country. There are already best practices about their management including those that have been documented in past studies on sustainable transport (e.g., San Fernando, La Union, Quezon City, Olongapo City, Davao City, etc.). Many of these cities are highly urbanized and would need to deal with all public transport and might just be the most knowledgeable and experienced in their jurisdictions. National government should at least identify pilot cities where bus, jeepney and van transport planning, franchising and management (including operations and enforcement) can be devolved or delegated. That is so we can already have an idea how these local transit authorities can be operationalized. Many already have their Local Public Transport Route Plans (LPTRP) so that is a good starting point for LGUs to establish their transit units around.
–
Another look at the ‘avoid, shift and improve’ framework
The transport and traffic situation during this pandemic has revealed a lot about what can be done and what needs to be done about transportation. Discussions about what and how people visualize their ideal or acceptable transportation system reminded me of the backcasting concepts and the tools. The following diagram is sourced from the SLoCaT homepage: https://tcc-gsr.com/global-overview/global-transport-and-climate-change/
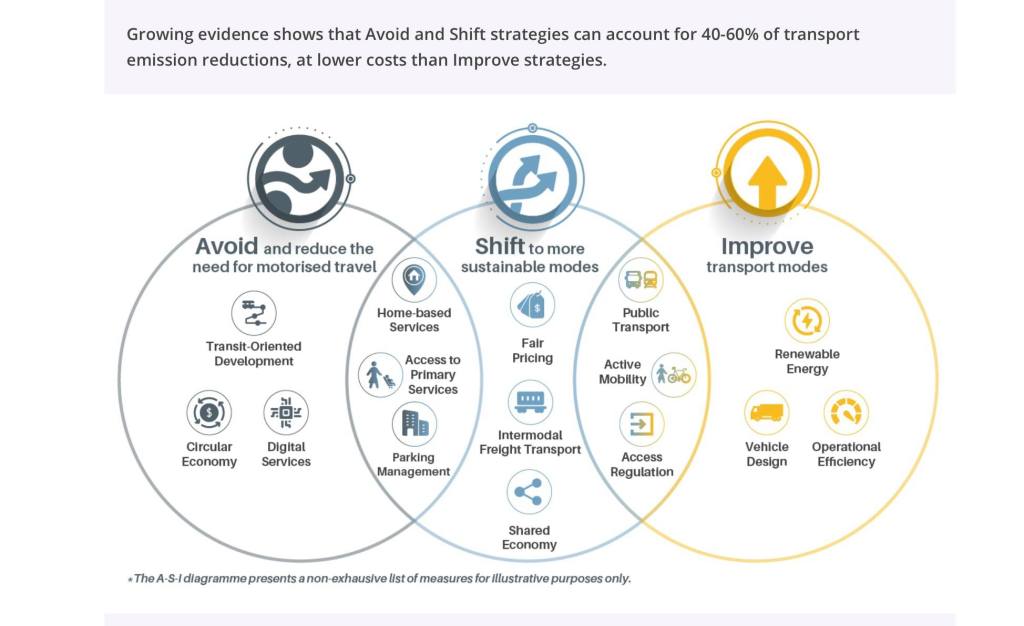
Note the overlaps among the three? Do you think its possible to have a measure that’s avoid, shift and improve at the same time?
Note, too, that if we contextualize this according to the Covid-19 pandemic, these measures even make more sense rather than appear like typical, ordinary measures we have about transportation. The pandemic revealed many weaknesses or vulnerabilities of our transportation system. We are presented with the opportunity to address these and implement certain measures that would have met with a lot of opposition before but can probably be rolled out now such as public transport priority schemes and protected bike lanes. “Work from home” is not really new since the concept has been proposed and implemented before but not as widely as was required by the pandemic situation. So perhaps we should take advantage of this forced reboot of sorts for our transportation system to be able to implement this A-S-I framework.
–
On car ownership and car use vs. public transport use
Here is another quick share of an article regarding car ownership and car use vs. public transport use. It is written in the first person as a the author relates her experience and what contradictory feelings she’s had with the decision to acquire and use a car.
Noor, D (June 21, 2021) “Buying a Car Improved My Life. It Shouldn’t Have.” Gizmodo, https://gizmodo.com/buying-a-car-improved-my-life-it-shouldnt-have-1847106068 [Last accessed: 7/10/2021]
I think many people in the Philippines (not just Metro Manila or other highly urbanized cities in the country) have similar experiences. They really don’t want to get a car or a motorcycle but their circumstances and the conveniences have outweighed their initial stand. Why do we need to have our own private vehicle anyway? Is it because its difficult to get a ride using public transport? Is it because of the quality of the ride? Is it due to health or safety-related reasons? In that last question, perhaps the fears of getting infected by Covid-19 present a overwhelming justification for car use and not just car ownership.
We also have to distinguish between vehicle ownership, car ownership and car use. ‘Vehicle ownership’ is a more general term that should include both motorized and non-motorized vehicles. Thus, if you have don’t have a car but instead have a bicycle, you are still a vehicle owner. Of course the term is more widely applied to motor vehicle owners but we need to expand this and distinguish between motor and non-motor vehicle ownership. Otherwise, let’s just be specific about the vehicle. ‘Car ownership’ is not equal to or does not correspond with car use. It is possible that one owns one or more cars or vehicles but does not use them at least for his/her regular commute. People in Singapore, for example, have cars. The same for people in Japan. However, most of these car owners choose to take public transportation most days. In their case, owning a car may not have improved their lives considering the excellent public transport services they have and requirements for people wanting to own cars in those places. Elsewhere, such as the Philippines, owning and using a car may provide better transport options depending not the circumstances of the person(s), even considering the costs of ownership and operations.
–
Modernized jeepneys in Marikina
Passing through Marikina City on the way home, I chanced upon these versions of the so-called modernized jeepneys plying routes in the city. Marikina has some of the oldest routes I’ve known including those originating from Parang and SSS Village. These were at the edges of the city and back in the day were bordering on rural as compared to the urbanized areas what was then still a municipality. The opportunity presented itself so I took a few photos of the mini-buses posing as jitneys or modern jeepneys.
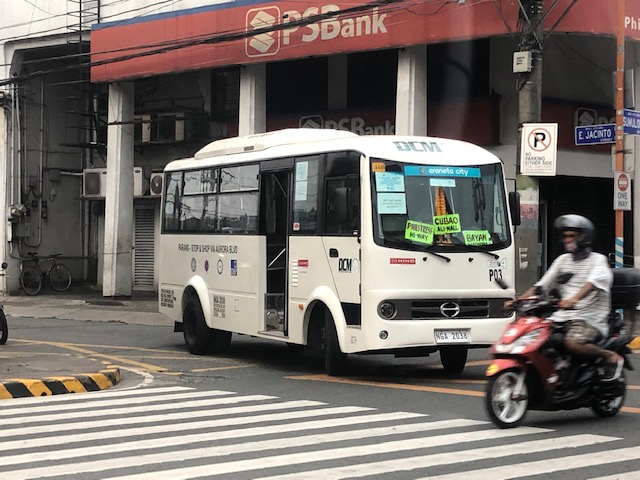
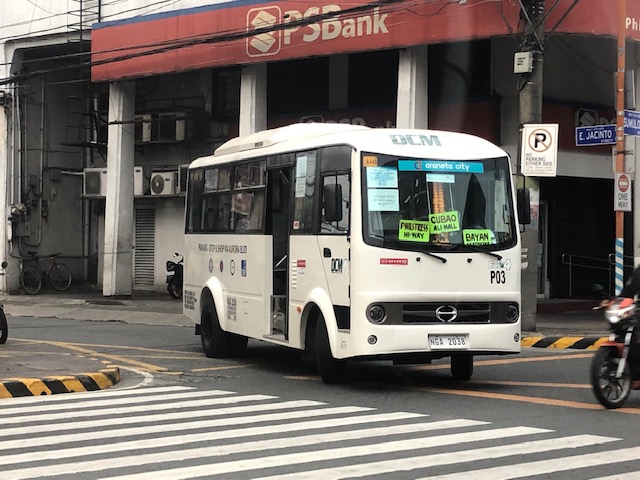



Unlike the old, conventional jeepneys, these are closed, air-conditioned vehicles. While there exists concerns about virus spread in such configurations, one cannot argue vs. the improved comfortability of these vehicles over the old ones especially when the Covid threat is already addressed. The vehicles seat 20+ passengers on average with more room for standees, if required and allowed in the future.
These vehicles are operated by transport cooperatives, which are encourage by the government in their PUV modernization program. Cooperatives have many advantages compared to the old set-up of individual operators. These include the personality or modality to engage financing institutions for acquiring fleets of PUVs. As such, modernization (or the replacement of old PUVs) is expedited. Note the logos along the side of the vehicle? These are DOTr, LTFRB, LTO and DBP. DBP is, of course, the Development Bank of the Philippines, which is one of the underwriters of the modernization program.
More on these vehicles, modernization and rationalization in future posts.
–
Updated fares for LRT Line 2
After so many years, the Line 2 extension to Masinag Junction is finally complete and operations covering the additional 2 stations. The 2 stations will be fully operational on June 23, 2021 (Wednesday) though there will be a ‘soft opening’ on June 22, 2021, following ceremonies for the extension. Here’s the new fare matrix showing how much passengers would have to pay traveling between certain stations including the two new stations of the extension – Marikina Station (formerly Emerald Station) and Antipolo Station (formerly Masinag Station):

What’s next for Line 2? Will there be another extension? Will there be a branch line? Also, it would be nice to see in the next few months if people will indeed be taking Line 2 instead of their current or usual road transport mode. Of particular interest would be if people will be shifting from private vehicle use. This is important because one main objective of the line is to reduce car dependence. That is expected to lead to a reduction in road traffic condition along the corridor (Marcos Highway and Aurora Boulevard). This could also provide lessons for Line 7, which is still under construction.
–
On the arguments vs. free transit
Here is a quick share of an article discussing about the idea of free public transport (no fare or minimal fares):
Grabar, H. (June 1, 2021) “The Problem with Free Transit,” Slate, https://slate.com/business/2021/06/free-transit-is-not-a-great-idea.html [Last accessed: 6/16/2021]
Apparently, “better transit, not cheaper transit” should be the mantra for both providers (operators including government) and users (commuters). It is a very sensitive topic for regulatory bodies though since higher fares are generally unpopular to the commuting public. One transport official recently stated that fare setting is a political issue. I tend to agree with this but only because the riding public is currently still largely ignorant or unappreciative of the benefits of efficient public transportation. Perhaps this is also because we’ve really had no efficient public transportation such as the ones we see in other countries including Singapore and Hong Kong? In Singapore, for example, the road pricing policies have educated people about the true costs of transport and that convinces most to take public transportation over private cars.
–
Are roads really designed just for cars?
The answer is no. Roads were and are built as basic infrastructure for transport no matter what the mode. However, the standards for dimensions (i.e., number of lanes, widths, etc.) are based on the motor vehicle capacity, and structural standards (i.e., thickness, strength, reinforcement, etc.) are based on the weights they are supposed to carry over their economic lives. The pavement load as it is referred to is usually based on the cumulative heavy vehicle traffic converted in terms of the equivalent standard or single axles or ESA. An ESA is 18,000 pounds or 18 kips in the English system of measurements or 8.2 metric tons in the Metric system.
 A typical local road – is it really just for cars or is it also for walking and cycling? Or perhaps animal drawn transport?
A typical local road – is it really just for cars or is it also for walking and cycling? Or perhaps animal drawn transport?
A colleague says many of the posts in social media pitting bicycles with cars are already quite OA (overacting). I tend to agree as I read how people generalize roads being car-centric. Roads have been built basically to serve a avenues for transportation. They were improved over time in order to have more efficient ways to travel by land. It didn’t hurt that vehicle technology also developed over time and bicycles somehow became less popular than the cars and motorcycles. The motorcycle itself evolved from bicycles so in a way, it is the evolved and mechanized form of the two-wheeler.
In a perfect world, people would be sharing the road space and it would be equitable among different users. In a perfect world perhaps, it won’t be car-centric as there would probably be better public transport options and transit will be efficient, reliable, comfortable and convenient to use.
The reality, however, is that we do not live in a perfect world and transformations like the ones being pitched on social media are nice but are also not as inclusive and equitable as their advocates claim them to be. I’ve always said and written that you cannot simply change transportation without also implementing changes in land use and housing in particular.
Why do we need wide roads connecting suburbs and urban areas? Why is there sprawl? Why do people live in the periphery of CBDs or the metropolis? It is not just about transport though it seems easier to focus on this. Even transportation in Japan, with Metropolitan Tokyo and its equivalent of NCR plus as a subject, needs to be properly contextualized for land use and transport interaction and development. It seems that even with a comprehensive and efficient railway network, there are still shortcomings here and there. We don’t have such a railway network (yet) so we need to find ways for easing the currently long and painful commutes many people experience on a daily basis. That means continued dependence on road-based transport and trying to implement programs and schemes to improve operations.
–
