Home » Railways (Page 2)
Category Archives: Railways
Cashless payment methods for public transportation
It took some time but finally there are even more options to pay for your transit fare, at least for MRT Line 3 for now. Here is the graphic from the announcement by the DOTr:

Hopefully, these methods will be available to all rail lines including the PNR. Hopefully, too, these options will be available in buses and perhaps at least on modern jitneys. This will make it easier to pay public transport fares for the regular transit users.
–
Transport options between Naga and Legazpi
I wrote about the PNR still operating between Naga and Legazpi cities. However, there is only one roundtrip per day and that is the Legazpi-Naga-Legazpi trip. If you want to do the Naga-Legazpi-Naga trip, you have to spend at least the night in Legazpi. But the latter schedule is not so good for the return to Naga as the train leaves Legazpi at 4:30 AM! Aside from the rail option, most people will use road-based transport. That is, most people will probably take a bus or van. There are many bus companies and UV Express vans operating along the corridor (Pan Philippine Highway) connecting the major cities and municipalities of the Bicol Region.
 We saw this van parked along the roadside as we were waiting for our turn to proceed along a section under construction employing a alternating one way traffic scheme.
We saw this van parked along the roadside as we were waiting for our turn to proceed along a section under construction employing a alternating one way traffic scheme.
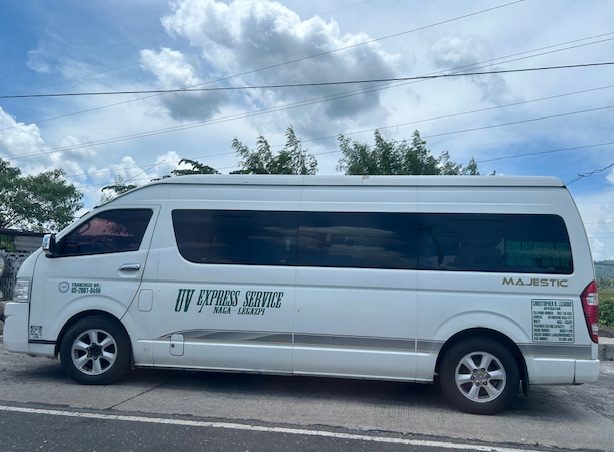 A close-up showing the UV Express van’s end points to be Naga and Legazpi. The declared passenger capacity is 23. Though this appears to be a long or stretched van, I can only imagine how comfortable or uncomfortable it is to ride these for 3 plus hours one way.
A close-up showing the UV Express van’s end points to be Naga and Legazpi. The declared passenger capacity is 23. Though this appears to be a long or stretched van, I can only imagine how comfortable or uncomfortable it is to ride these for 3 plus hours one way.
More on Bicol transportation in my posts this coming July!
–
PNR services from Naga City
I have yet to share the photos I took at the PNR Station in Naga City. Instead, I am sharing here the current train schedule and fares.
 There are only three trips from Naga to Sipocot – two in the morning and one in the afternoon. Meanwhile, there is only one trip to Legazpi. Sipocot is in the same province, Camarines Sur, while Legazpi is the capital of Albay.
There are only three trips from Naga to Sipocot – two in the morning and one in the afternoon. Meanwhile, there is only one trip to Legazpi. Sipocot is in the same province, Camarines Sur, while Legazpi is the capital of Albay.
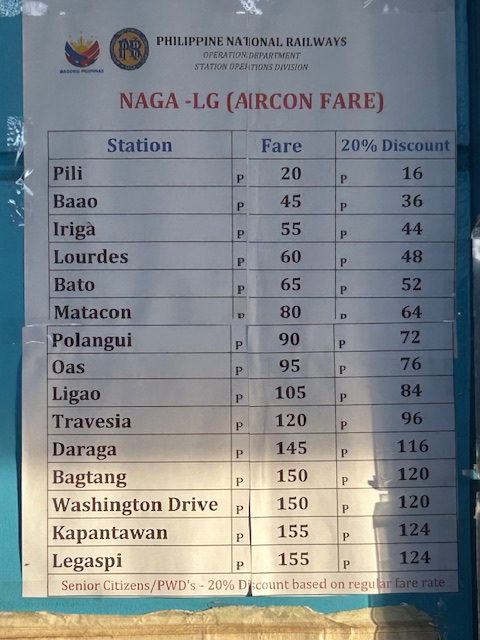 Fare rates between Naga City and Legazpi City. There are 15 stops along this route.
Fare rates between Naga City and Legazpi City. There are 15 stops along this route.
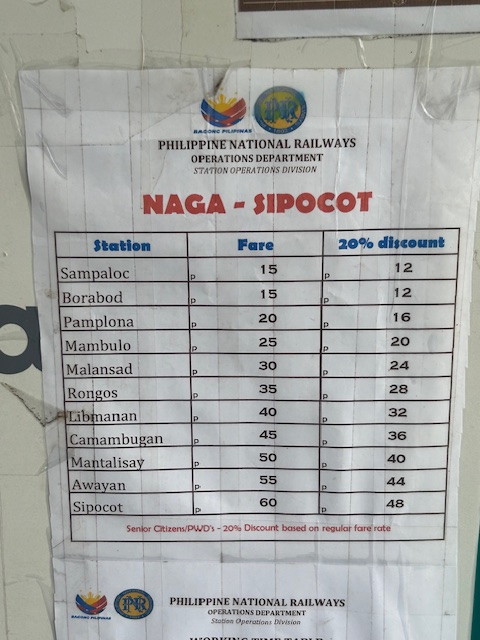 Fares for destinations between Naga and Sipocot
Fares for destinations between Naga and Sipocot
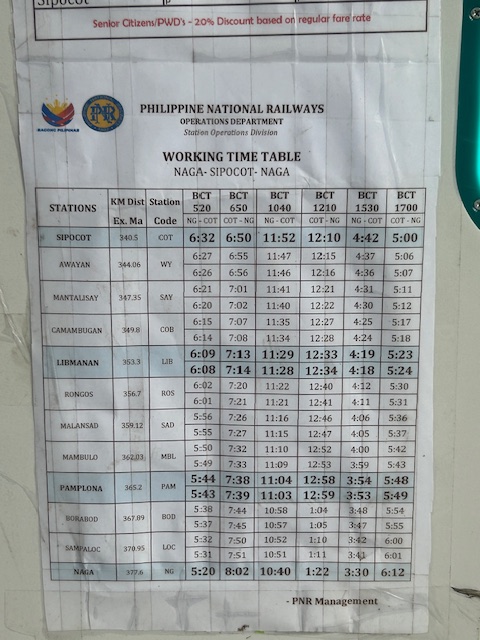 Timetable between Naga and Sipocot. It takes 1 hour and 12 minutes one way. It seems I wasn’t able to take a photo of the Naga-Legazpi timetable but the staff told us it takes 3 hours to get to Legazpi.
Timetable between Naga and Sipocot. It takes 1 hour and 12 minutes one way. It seems I wasn’t able to take a photo of the Naga-Legazpi timetable but the staff told us it takes 3 hours to get to Legazpi.
The station staff also told us that the train from Legazpi leaves at 4:30 AM. If it also takes 3 hours, then it arrives in Naga at 7:30AM. This can be okay for a super-commuter even at this travel time and speed (about 33 km/h). The frequency of trips between Naga and Legazpi should increase and will probably do once the PNR completes rehabilitation of what was termed as the Main Line South.
–
Quick comments on the NCAP
The No Contact Apprehension Policy (NCAP) is finally being implemented in Metro Manila. The results so far has been dramatic in terms of the number of violations recorded and the images being shared so far about how motorists are behaving. Below is one of those photos being shared on social media to which I added some annotations. I will use this later to comment on the NCAP and how we can use the outcomes to assess the transportation situation and determine what interventions can be done. Some are already obvious from the photo – the lack of public transport options lead to people depending on private motor vehicles like cars and motorcycles for their commutes. MRT7 is yet to be operational and road public transport has not been rationalized.
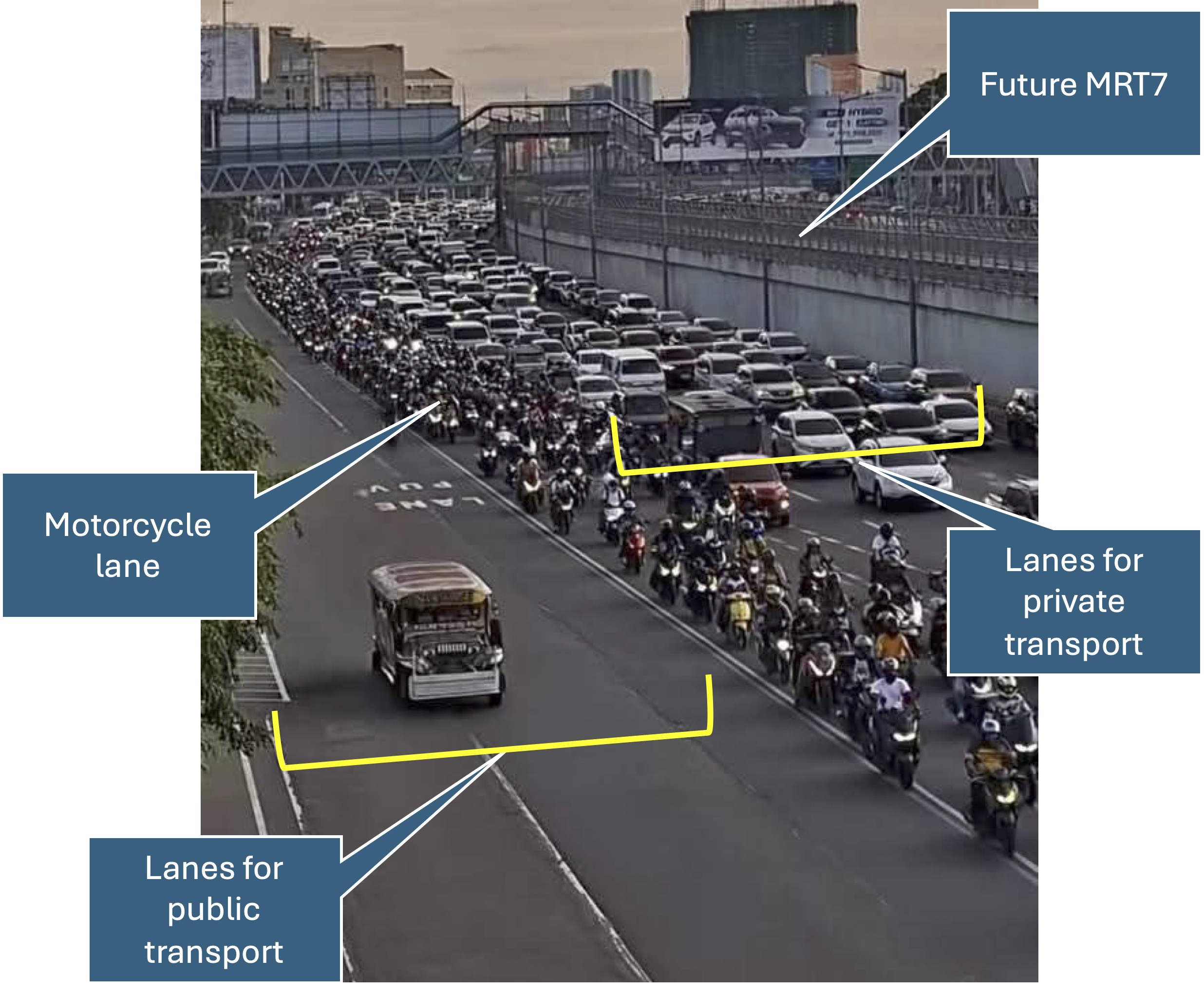
More on this topic soon!
–
Metro Manila rail network by 2030?
I saw another map circulating in social media. It would really be nice to have a more comprehensive rail network for Metro Manila or perhaps the Greater Capital Region (Mega Manila or NCR plus or whatever you want to call it). Maps like this give us something to look forward to. We are made to be hopeful about our places being served by trains just like what some of us have experienced abroad in cities like Singapore and Tokyo.
Credits are due to whoever made this map. While it has the DOTr logo, I am not sure someone from there made the map. There are many ‘mapmakers’ out there who can make transit maps like this.
–
Solutions to transport problems: the combination of congestion pricing and transit infrastructure development
Congestion pricing and transit infrastructure development (e.g., mass transit infrastructure) are often mentioned separately or independently. It is as if they are mutually exclusive alternatives or solutions to our transportation problems. They are not and should be considered together for greater impacts and also to complement each other. While the article below focuses on the experience in the United States, the experience is Singapore as applied to cities should provide a model that can be adopted if not outrightly replicated. Singapore’s version of congestion pricing in the form of its Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) scheme has been very effective in regulating congestion levels while helping fund public transportation in the city-state.
Descant, S. (May 8, 2025) “Congestion Pricing and Transit Are a Necessary Alliance,” Government Technology, https://www.govtech.com/transportation/congestion-pricing-and-transit-are-a-necessary-alliance %5BLast accessed: 11/05/2025]
Quoting from the article:
“In order to move a congestion pricing proposal forward, “you must have serious congestion, and you must have good transit,” said Sam Schwartz, a former New York City traffic commissioner, said during a March 21 panel on the New York City congestion pricing program. The event was organized by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Mobility Initiative. Schwartz is also the CEO of Sam Schwartz Pedestrian Traffic Management Services, a consulting firm.
A recent report by the Mineta Transportation Institute at San Jose State University in California concluded roadway tolling — a form of congestion pricing — can serve the dual purpose of reducing traffic congestion and supporting transit options, if the programs are structured properly.”
–
To B(RT) or not to B(RT)?
I kind of expected questions or comments from my ‘students’ after my lecture last Wednesday about “Traffic Congestion.” Among my slides were those featuring solutions to transport and traffic problems. I presented both soft and hard approaches including travel demand management schemes and infrastructure that we should have built decades ago. The uniformed officers who were there had a very simple take on congestion – it’s basically because of a lack of discipline. While theirs may also be valid observations based on their experiences, ‘discipline’ is not the most critical problem that we have especially considering the ever increasing demand for travel. One government official present was very direct in his question about what I thought about the MMDA’s pronouncement that they plan to remove the EDSA Bus Carousel. I thought my reply and the following explanation was clear – it was a wrong move.
The EDSA Bus Carousel is simple. Bus lang sa bus lane (Only buses along the bus lane). Pag may private or pa-VIP, bawal at huli dapat (If there are private vehicles or those who regard themselves as VIPs using the lane, then they should be apprehended. An HOV (high occupancy vehicle) lane is more difficult to implement. Mas pahirapan ang pag monitor and enforce (It is very difficult to monitor and enforce). So this proposal to phase out the EDSA bus lanes don’t make sense from this perspective. In fact, I don’t agree with a couple of more senior transport experts who say that the MRT Line 3 is sufficient and that it hadn’t reached capacity yet. It has but in the time that the carousel has been operational, the carousel had absorbed much of the demand along the corridor. There is also the fact that it will take much time before Line 3 is upgraded. Are the new train sets here? Are the stations designed for these trains and more passengers? If the answers are no, then MRT3 will not have its capacity increased in such a short time. That also means the carousel is very much relevant not just to supplement MRT3 capacity but as a needed alternative mode for commuters.
–
Roads, railways support needed for airport upgrades — analysts
Here’s a quick share on an article on the infrastructure needed to support airport development:
Source: Roads, railways support needed for airport upgrades — analysts
Unlike many capital airports including Malaysia’s Kuala Lumpur International Airport and Bangkok’s Suvarnabhumi International Airport, Ninoy Aquino International Airport does not have rail or mass transit access. It will eventually have rail access via the currently under construction Metro Manila Subway. The airport construction in Bulacan should also have transit access in order to make it more accessible to passengers and other airport users. Railways will provide an alternative to road-based transport that would probably require much road space and likely lead to congestion just like what we experience around NAIA at present.
–
The journey to PHL’s railway renaissance
Here is a quick share of an article on railway development in the Philippines. It certainly took a while for railway development to get underway with considering rail transit would probably had a major impact on commuting particularly in Metro Manila and highly urbanized cities like Cebu and Davao that require mass transit systems to alleviate congestion.
Source: The journey to PHL’s railway renaissance
The article though doesn’t contain a narrative on the journey but rather only a summary of the rail projects that are currently being implemented as well as those in the pipeline. It would be a nice to have a more historical approach to this so-called journey so we can have an objective look at what happened to our railways from the 1970s when its decline began until the last few years when a so-called renaissance came to be.
–
On “levelling-up” on fare collection
I found this article on how Japan Railways East (JR East) plans to upgrade its Suica card so passengers don’t need to swipe them at the stations. That will mean practically seamless entries and exits at the stations and perhaps the elimination of most queues related to this part of rail operations. Here is the article published on Medium:
To quote from the article:
“You can currently use Suica to pay for goods and services at around 2.26 million locations in Japan. However, JR East has only issued around 31.47 million mobile Suica cards. That lags behind the two most popular cashless payment options — PayPay (66 million) and d-Barai (63 million).
The move comes as transportation cards, long a staple of travel inside of Japan, seem to be going out of style. More train companies are introducing QR code and credit card touch payment options, making the one cutting-edge technology obsolete.”
I have a Suica card as well as others like it from Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur and Singapore. Suica has really been a convenient way to pay transport fares as well as to purchase items such as drinks or snacks particularly at train stations in Japan. We are not yet at the level of the Suica card of more than ten years ago but there are lessons to be learned here in case we finally have something like it and others that make travel or commuting easier.
–

