Home » Posts tagged 'sustainable transport' (Page 2)
Tag Archives: sustainable transport
On the impact of bike lanes on motor vehicle traffic
With the news that bike lanes will be removed along major roads including, most recently, I share some findings from the US about a decrease in traffic speeds when there are protected bike lanes. The decrease in speeds are associated with a reduction in road crashes, ergo safer streets.
McPherson, K. (June 3, 2024) “Traffic Speeds Decrease When Bike Lane is Present,” Rutgers.edu, https://www.rutgers.edu/news/traffic-speeds-decrease-when-bike-lane-present [Last accessed: 6/8/2024]
To quote from the article:
“They found that the presence of the delineated bike lane made a difference: a 28 percent reduction in average maximum speeds and a 21 percent decrease in average speeds for vehicles turning right. For those heading straight and not turning, a smaller speed reduction of 8 percent was observed. In addition, drivers moving at a perpendicular angle to the bike lane did not slow down.
Marking the bike lanes with cones as a clearly delineated space was more effective at reducing speed than a painted-only bike lane. The painted-only bike lane was associated with a smaller speed reduction of between 11 percent and 15 percent, but only for drivers turning right.
Younes hypothesized that drivers slow down when they see a bike lane marked with the cones because the driving lane is narrower and requires more concentration, and it’s easier to notice cones or planters or some other space delineator than it is to spot painted lines on the road surface.”
Of course, one major element that was probably not considered in their studies is the presence and behavior of motorcycle riders. Motorcycles here frequently enter and use bike lanes whether protected or not. Often they crowd out bicycle users leading to situations where riders of motorized and non-motorized 2-wheelers come into conflict. Still, it would be nice to have a study to determine not just whether there are similar outcomes here but to what extent as well as how motorcycles figure in the study.
–
Another roadblock for active transport?
The Metro Manila Development Authority (MMDA) recently released what they claim to be their counts of bicycle traffic along major roads in Metro Manila from 2020 to 2023.
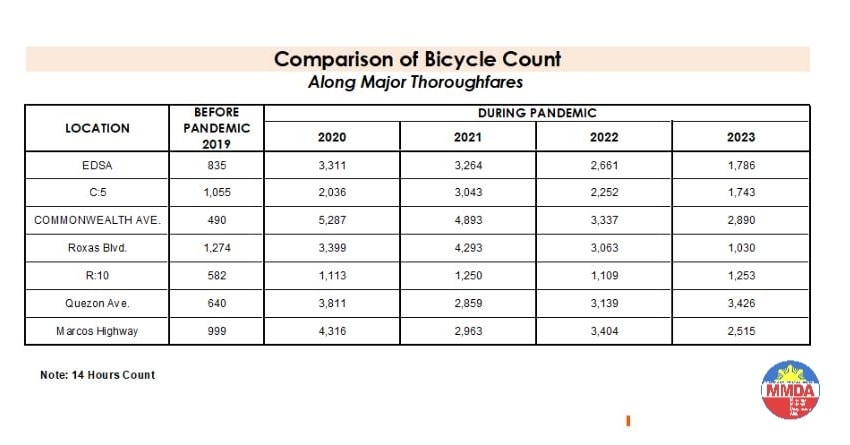
These are supposed to be official data as it is issued by the government agency in-charge of traffic management for Metro Manila roads (aside from its other functions and roles). What are not stated, and are actually very important details, are the locations of the counts and when the counts were conducted. The Traffic Engineering Center (TEC) that was under the DPWH and currently with the MMDA used to publish traffic volume maps for major roads in Metro Manila. So along EDSA, for example, the volume per section are shown on the map. The same for other major roads like Commonwealth, Quezon Avenue and SLEX. The thicker lines mean higher volumes along those sections, and vice versa. However, they did not consciously count bicycles (only motor vehicles) and perhaps MMDA only started counting during the pandemic (i.e., 2020). So there is no one value to represent a road. And counts vary over time of day, day of the week and even throughout the year (i.e., monthly variations).
There were many reactions to the MMDA’s posting of the data and most were critical and even derided the agency for what to them appeared to be inaccurate data. The problem is that it seems there are no other counts that can validate and perhaps refute the MMDA data. Previous bike counts were not conducted according to how the MMDA and DPWH count vehicles. That is, counts are typically done over a 14 or 16-hour period and ideally on several days in a year. Expansion and conversion factors are applied based on established stations along major roads that are supposed to have more frequent if not continuous counts. This methodology is how Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) is computed. Call it car-centric if you like but the methodology is very much applicable to bicycles as well. Peak hour counts for bikes are not enough and the peak hour factor for motor vehicles does not apply to bicycles (if this is to be used to expand/convert peak volumes to daily values). In fact, if you go into the math, there should be a peak hour factor for each type of vehicle considering each vehicle’s volume will vary differently over time. So yes, the solution here is to conduct bicycle counts according to how MMDA or DPWH counts vehicles and these should be done along several stations along major roads (e.g., those in the table above) to validate the MMDA counts.
More on this topic in the next post!
–
Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here is a quick share of another very informative article that discusses the importance of proximity and more dense development in order to reduce car dependence.
Source: Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here are some excerpts from the article:
“This shows that proximity is much more important than mobility in providing accessibility: location, location, location. For the last century, our transportation planning practices have contradicted this principle. Transportation agencies built urban highways that destroyed and degraded accessible and multimodal neighborhoods to benefit suburban motorists. This was racist and classist, but the mechanism was the way that transportation planners valued increased traffic speeds, measured as travel time savings, while ignoring the loss of accessibility imposed on urban neighborhood residents.
Of course, many other factors affect people’s transportation and neighborhood preferences. Some people need their cars for work or after-work activities, and not everybody can bicycle or use transit even if it is available. However, surveys such as the National Association of Realtor’s National Community Preference Survey indicate that many people would prefer living in more compact, walkable neighborhoods than they currently do but cannot due to a lack of supply.”
Such articles are a must read for those who want to understand why government needs to invest in land at or near the CBDs, and develop that land so people will not need to reside far from their workplaces and schools. Truly, there are many other factors affecting transport preferences or mode choice. Housing is one such factor that we continue to treat separately from transport. It is very (prohibitively) expensive to buy or rent in the city particularly in or near the CBDs. The result is people opting to purchase or rent homes in the suburbs. It doesn’t help that developers are also actively promoting subdivisions there and therefore are contributing to sprawl that puts so much pressure on transportation systems.
–
30th Conference of the Transportation Science Society of the Philippines
I am sharing here the First Call for Papers for the 30th Annual Conference of the Transportation Science Society of the Philippines (TSSP). The conference will be held in Iloilo City almost to the day of the last time it was held there in Sept. 12, 2014.

Information on past conferences may be found here: https://ncts.upd.edu.ph/tssp/conferences
–
More than just painted lines – good practice examples of bike lanes
I’m sharing this article on the best bike lanes in the United States:
Holbrook, A. (February 12, 2024) “The 5 Principles That Make America’s Best Bike Lanes: A Lot More Than Painted Lines,” Velo, https://velo.outsideonline.com/urban/urban-gear/five-principles-the-best-bike-lanes/ [Last accessed: 2/15/2024]
This is a follow-up on an article on the best new bike lanes or bikeways that I shared earlier. This article features an interview of the author of the previous article about what features distinguish these bike lanes over others that have been implemented. Definitely, bike lanes should be designed beyond the usually painted lines that offer little protection to cyclists.
Here are examples of bike lanes in the Philippines:
 Painted bike lanes along Ortigas Avenue Extension, Cainta, Rizal
Painted bike lanes along Ortigas Avenue Extension, Cainta, Rizal
 Protected bike lane along Katipunan Avenue (C-5), Quezon City
Protected bike lane along Katipunan Avenue (C-5), Quezon City
–
On the Pasig River esplanade project
My news feed was full of articles on the Pasig River esplanade, or at least the recently completed section at the Manila Central Post Office building. This is a proof of concept type of project that hopes to be expanded or extended to cover both sides of the river much like the Iloilo River Esplanade project. If you are wondering what the section looked like before the project, here are two posts I wrote in 2012 that features a lot of photos of the Muelle del Rio:
These were way before the fire that damaged the Post Office building. However, even at that time, there were already calls for the renovation, even repurposing of the Post Office building. Such projects or proposal draw inspiration from Singapore where old buildings have been preserved and many repurposed (e.g., how about the Post Office building transformed into a hotel?). Perhaps such will breathe life and lead to a revival of this part of Manila?
–
On bike lanes network development – examples in the US
I am sharing this article on the best new bike lanes in the United States:
Haggerty, M. (January 12, 2024) “The Best New U.S. Bike Lanes of 2023,” People for Bikes, https://www.peopleforbikes.org/news/the-best-new-u.s.-bike-lanes-of-2023 [Last accessed: 1/23/2024]
Quoting from the article:
“Even for the most ardent naysayers, it’s difficult to deny that the landscape of bicycling in America is transforming (although not as quickly as many of us would like to see). While we have yet to see any U.S. cities emerge with truly bold citywide plans for bike networks as we’ve seen in places like London, Paris, and Bogota, many are (slowly) beginning to envision a future where cycling takes center stage. Although there remains a substantial amount of work ahead of us to cultivate a safe and comfortable environment for people of all ages and abilities to ride bikes in the U.S., it’s well worth pausing to commemorate the significant infrastructure victories U.S. cities achieved in 2023.”
The quote above also applies to us in the Philippines where there are still few examples of safe and comfortable bike lanes. I shared the same article on my social media page asking aloud if there’s something like this in the Philippines. I am aware of the Mobility Awards but that’s supposed to cover everything on mobility and particularly walking and cycling. The list is about bike lanes and touches on the various designs (note that in the US, while there are federal guidelines, most if not all states and cities would have their own that they use for planning and design of bicycle facilities). It would be nice to have our cities develop guidelines while also referring to the minimum standards in the DPWH Guidelines. Of course, the challenge is to come up with good if not the best designs and not just comply with the minimum.
 If there was an award for best new bike lanes in 2023, I think Quezon City will have several nominees and even win the award with one. Picture above is the bike lane along Katipunan Avenue/C5.
If there was an award for best new bike lanes in 2023, I think Quezon City will have several nominees and even win the award with one. Picture above is the bike lane along Katipunan Avenue/C5.
–
On reimagining our streets
We start the last month of the year by sharing this article on complete streets:
Robertson, D. (November 15, 2023) “Safe streets are global—and it’s time for the U.S. to catch up,” Smart Growth America, https://smartgrowthamerica.org/safe-streets-are-global-and-its-time-for-the-u-s-to-catch-up/?eType=EmailBlastContent&eId=03b04320-4eeb-4bf5-9b12-71ec2a960421 [Last accessed: 12/1/2023]
To quote from the article:
“The examples mentioned here are exemplary cases, but demonstrate that the future of mobility need not follow the same dangerous status quo. They prove that with a combination of public and political will to the commitment of the prioritization of people over cars, we can produce the results we care all about.”
While the article is on complete streets, there is a very quotable section that referred to the situation in Japan:
“Anyone who wants to register a car in Japan today must prove that they have a private place to park it. This shifts the economic burden of providing parking from the public to drivers, and also ensures that supply of parking will not grossly outpace demand.”
There are many opportunities for the complete streets concept to be applied in the Philippines. A few have already been implemented but there should be more especially in light of the gains from the development of bike lanes networks in many LGUs that started during the COVID-19 pandemic. As for parking, perhaps the Japanese example should be adopted and implemented to curb car-dependence.
–
Article share: On the benefits of sidewalk networks
Here is another quick share of an article by Todd Litman on Planetizen. The article contains a lot of information or data about why we should be investing in sidewalks or pedestrian facilities (i.e., for walking).
Litman, T. (August 6, 2023) “Completing Sidewalk Networks: Benefits and Costs,” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/blogs/124999-completing-sidewalk-networks-benefits-and-costs?utm_source=newswire&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=news-08142023&mc_cid=cd3b2e2ba5&mc_eid=9ccfe464b1 [Last accessed: 9/23/2023]
To quote from the article:
“Walking is the most basic and universal travel mode, and sidewalks are the most basic walking infrastructure, but they are often overlooked and undervalued in transportation planning. Completing and improving sidewalk networks can help achieve many economic, social and environmental goals.
Recent case studies indicate that typical North American communities spend $30 to $60 annually per capita on sidewalks, and would need to double or triple these spending levels to complete their networks. This is a large increase compared with current pedestrian spending but small compared with what governments and businesses spend on roads and parking facilities, and what motorists spend on their vehicles. Sidewalk funding increases are justified to satisfy ethical and legal requirements, and to achieve various economic, social and environmental goals. There are several possible ways to finance sidewalk improvements. These usually repay their costs thorough savings and benefits.”
–
On reducing vehicle travel
This Sunday, I am sharing this article on the reduction of excess vehicle travel. I noted the use of the word ‘excess’ here, which somewhat distinguishes what is excess from what is necessary vehicle (or car) use.
Litman, T. (September 8, 2023) “How to reduce excess vehicle travel,” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/blogs/125445-how-reduce-excess-vehicle-travel?utm_source=Planetizen+Updates&utm_campaign=b3ced8c873-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2023_08_09_05_38_COPY_01&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_-6cce27a957-%5BLIST_EMAIL_ID%5D&mc_cid=b3ced8c873&mc_eid=9ccfe464b1 [Last accessed: 9/17/2023]
To quote from the article:
“Too often, practitioners undercount and undervalue slower but more affordable, inclusive, and resource-efficient modes such as walking, bicycling, and public transit. This contributes to the self-reinforcing cycle of automobile dependency and sprawl, illustrated below. We have an opportunity to break this cycle by recognizing the unique and important roles that walking, bicycling, and public transit can play in an efficient and equitable transportation system, and the cost efficiency of vehicle travel reduction policies. Telework can help, but only if implemented as part of an integrated program to create a more diverse, efficient and equitable transportation system.”
There is a lot you can pick up from this article, which sheds a light of hope towards addressing the most pressing issues particularly for our daily commutes. Litman is always clear and evidence-based for his discussions. His arguments are very persuasive if only decision-makers are not resistant to the facts about transport.
–
