Home » Economics (Page 2)
Category Archives: Economics
On a ‘tipping point’ for bikeability in cities
Here’s a nice article on bikeability and pertains to cities in the United States that developed bikeways or bike lanes during the pandemic. Like many cities that have ‘discovered’ cycling as a viable mode of transport particularly for commuting during the COVID-19 pandemic, it is postulated that there would be a threshold when people would switch to cycling and/or demand for more cycling facilities.
Wilson, K. (June 25, 2024) “Has Your City Passed the ‘Bikeability Tipping Point’?,” StreetsBlog USA, https://usa.streetsblog.org/2024/06/25/has-your-city-passed-the-bikeability-tipping-point [Last accessed: 7/2/2024]
To quote from the article:
“A whopping 183 American communities achieved a score of 50 or higher on PeopleForBikes annual City Ratings this year, up from just 33 in 2019. The means 183 communities have scored at least half of the available points on the group’s signature “SPRINT” rubric that includes such measures as protected bike lanes, safe intersection treatments, and reduced speed limits that are unlikely to kill a cyclist in the event of a crash, among other factors.
And when a city clears that 50-point threshold, the authors of the ratings say that its local bike culture has firmly taken root — and that every new roadway improvement will inspire more improvements, rather than a fierce fight against a car-dominated status quo.
“Once you’ve hit 50, your city probably has a pretty good low-stress bike network,” said Martina Haggerty, the senior director of local innovation at PeopleForBikes. “[That’s] not to say that there aren’t still improvements to be made [but it] probably means that more people are riding bikes in those communities because they feel safe and comfortable. And when more people start riding bikes, those people tend to become advocates for better bike infrastructure and for pro-bike policies, which, [in turn,] will get more people riding.”
There are many links found in the article itself that are “click worthy”. I recommend the reader to explore the rubric from PeopleForBikes and see for yourself how this can be adopted for your city. Is such a rubric applicable to the Philippines? Perhaps, but there would be a need to assess the the situation in each city or municipality. So far, there have been mixed reviews among cities, especially those that appeared to have been more progressive and were more aggressive than others in putting up bicycle facilities including bike lanes. Perhaps the rubric can be applied to see how our LGUs measure up?
–
On the idea of congestion pricing
I purposely titled this post to include the word ‘idea’ as congestion pricing is still very much like that in the Philippines. It is a reality in some part of the world particularly in Singapore where its Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) has evolved and improved over the years. Its success though seems to be an exceptional case that has not been replicated elsewhere where conditions are not exactly like the city state’s.
Here is an article that recently came out from The Washington Post about the New York Governor’s decision to backtrack on the proposed congestion pricing initiative in New York City:
McArdle, M. (June 12, 2024) “People hate traffic. They also hate this great idea to clear it,” The Washington Post, https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2024/06/12/congestion-pricing-great-idea-people-hate/ [Last accessed: 6/14/2024]
To quote from the article:
“Roads are a scarce good; you can fit only so many cars on a road at one time, and fewer if you would like those cars to go somewhere. When roads are “free,” we are forced to fall back on a more costly and inefficient strategy: sitting in traffic. This wastes valuable human time and inflicts noise and pollution on everyone nearby. Far better to charge a modest price that inspires some drivers to carpool and others to take public transit or shop nearer to home, until supply and demand are balanced and traffic flows easily…
In political disputes, a discrete group facing highly concentrated costs often defeats a larger public interest that conveys a small individual benefit to everybody — such as being able to move around the city faster when you really need to. This is particularly true in the American system, which is designed to empower angry minorities. And it’s especially true when they’re abetted by status quo bias and a sympathetic majority, as in this case.
Complain all you want about selfish suburban drivers or the Metropolitan Transit Authority’s bloated cost structure or Hochul’s cowardice; the biggest obstacle to congestion pricing is that almost two-thirds of New York City residents have told pollsters they oppose it — in a city where less than half of all households even own a car. A more technocratic, less democratically responsive government might have been able to ram it through, and perhaps in time everyone would have come to like it. But in fractious America, with all its political veto points, congestion pricing is doomed by the reality that people hate slapping prices on things — especially if they have to pay them.”
There is a congestion pricing proposal in Baguio City and we don’t know yet how this will go. I don’t have the details yet except that a private company whose core business is tollways is involved. Will this be a model or a proof of concept? Or will it just go the way of a typical tollway where users are those who are willing to pay and which would eventually congest if most of the current users pay and use it anyway? Will the funds generated be used to develop a more efficient transport system for Baguio, eventually leading and contributing to less congested streets? That would also mean eventually less revenues from the congestion pricing scheme and probably lead to it being unnecessary.
–
Article share: on making more affordable neighborhoods
I’ve been commenting about how transportation cannot be isolated and the need to relate it to other factors such as housing or home location choice. The latter though is also affected by other factors as well that affect the affordability of homes near the city centers or CBDs where workplaces and schools are located. The result of course is sprawl or the encouragement of sprawl. Private companies take advantage of this or contribute to this ‘encouragement’ by developing land farther away from the center. Thus, for Metro Manila’s case, many people reside in the peripheral provinces of Bulacan, Rizal, Laguna and Cavite. There are even those who choose to reside in Pampanga, Bataan and Batangas.
Kayatekin, C.S. and Sanmiguel, L.U. (April 16, 2024) ” ‘Urban form’ and the housing crisis: can streets and buildings make a neighborhood more affordable?” The Conversation, https://theconversation.com/urban-form-and-the-housing-crisis-can-streets-and-buildings-make-a-neighbourhood-more-affordable-224108 [Last accessed: 4/23/2024]
Quoting from the article:
“Our main finding was that the bottom-up districts we looked at had, overall, more small-scale apartments. The reason is simple: they had more small-scale buildings, built on small-scale plots. Once divided into apartments, this produces small apartments – homes in the bottom-up areas were 10% to 23.1% smaller than their top-down counterparts. This also made their real estate markets for small homes more competitive, and therefore more affordable.
However, our study showed there is nothing inherently magical about bottom-up areas. Their more intricate housing stock has little to do with the layout of streets and blocks, and a lot to do with how that land is built upon.
Plot size appears to be the deciding factor: the districts with greater numbers of small buildings built on small plots supported a denser and more affordable housing stock, regardless of whether they were top-down or bottom-up.
Older bottom-up areas seem to naturally lend themselves to having more small-scale plots. This is likely due to the incremental development of these areas, and the complex land ownership patterns that developed as a result. However, there is no reason why a top-down area cannot be designed to replicate these characteristics.”
–
When Driving Isn’t an Option: Steering Away From Car Dependency
Here is another quick share of an article from Planetizen. The article relates about people who cannot drive so driving for them is not an option:
Source: When Driving Isn’t an Option: Steering Away From Car Dependency
Quoting from the article:
“Zivarts shows that it is critical to include people who can’t drive in transportation planning decisions. She outlines steps that organizations can take to include and promote leadership of those who are most impacted—and too often excluded—by transportation systems designed by and run by people who can drive. “
There are actually many who can drive and who would like not to drive but then opt to drive because of limited and inconvenient or uncomfortable options. I think government agencies and local government units are supposed to work on this but like people who try to ‘solve’ traffic by isolating it from other factors such as housing, they ultimately gain little ground if not fail. It doesn’t help that the decision makers such as government officials and politicians drive or are driven. Of course, there is still such a thing as empathy so let’s not discount those who do use cars for their commutes but also work hard to improve transportation. It’s just that such people are rare these days and may not be in a position to move things to enable significant improvements to the transportation system.
–
Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here is a quick share of another very informative article that discusses the importance of proximity and more dense development in order to reduce car dependence.
Source: Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here are some excerpts from the article:
“This shows that proximity is much more important than mobility in providing accessibility: location, location, location. For the last century, our transportation planning practices have contradicted this principle. Transportation agencies built urban highways that destroyed and degraded accessible and multimodal neighborhoods to benefit suburban motorists. This was racist and classist, but the mechanism was the way that transportation planners valued increased traffic speeds, measured as travel time savings, while ignoring the loss of accessibility imposed on urban neighborhood residents.
Of course, many other factors affect people’s transportation and neighborhood preferences. Some people need their cars for work or after-work activities, and not everybody can bicycle or use transit even if it is available. However, surveys such as the National Association of Realtor’s National Community Preference Survey indicate that many people would prefer living in more compact, walkable neighborhoods than they currently do but cannot due to a lack of supply.”
Such articles are a must read for those who want to understand why government needs to invest in land at or near the CBDs, and develop that land so people will not need to reside far from their workplaces and schools. Truly, there are many other factors affecting transport preferences or mode choice. Housing is one such factor that we continue to treat separately from transport. It is very (prohibitively) expensive to buy or rent in the city particularly in or near the CBDs. The result is people opting to purchase or rent homes in the suburbs. It doesn’t help that developers are also actively promoting subdivisions there and therefore are contributing to sprawl that puts so much pressure on transportation systems.
–
Article share: on subsidies to public transportation
Here’s a nice article that presents arguments for subsidies to support transit or public transportation:
Wilson, K. (February 5, 2024) “Study: Subsidizing Transit Actually Makes It More Efficient,” Streets Blog USA, https://usa.streetsblog.org/2024/02/05/study-subsidizing-transit-actually-makes-it-more-efficient [Last accessed: 2/18/2024]
Subsidies to public transportation can be quite tricky and may require quite a balancing act. There seems to be few options outside of the straightforward subsidies national and local governments in the Philippines provide. Rail transit, for example, is heavily subsidized but these are rare for road-based public transportation. The concept of service contracting has been considered but it also has a few variations. While there seems to have been a proof of concept tested during the pandemic, it required so much funds that government apparently lost interest (i.e., the funds were also needed by other sectors). Local governments meanwhile, or at least those that had resources, decided to operate their own public transport (e.g., Quezon City bus).
To quote from the article:
“Newmark’s study doesn’t definitively determine why, exactly, high subsidies seem to correlate with better efficiency and transit agencies collecting more fares, but he has some theories. Some systems, he says, use subsidies to increase service frequency or install dedicated lanes to speed routes up along heavily-utilized corridors — and riders are responding, predictably, by showing up in droves. (Route expansion can help, too, he said, but only if agencies expand service to places “where there’s actual demand.”) Others use subsidies to keep ticket prices low, but not to eliminate fares outright, which Newmark argues is a smart move.
“People value stuff they pay for, and they pay for stuff they value,” Newmark added. “An underlying point in this paper is that transit offers something [valuable], and it’s worth trying to capture that value, whether through fares or in other ways.”
If transit networks and the taxpayers who support them can get that recipe right, it could create a virtuous cycle.
“If people see the benefits [of subsidies], that may make them more willing to invest [their taxpayer dollars],” he adds. “Good transit leads to a real social movement for more subsidies.” “
What do you think about subsidies to public transport in the Philippine setting? Of course, we are referring to ‘formal’ public transportation here. There are many ‘informal’ or paratransit modes like tricycles and non-motorized pedicabs. There are also motorcycle taxis providing services or filling in the gaps in transport services.
–
On micro transit covering for regular public transport services
I am sharing this very interesting (to me) article on microtransit making up for the conventional public transportation:
Zipper, D. (December 19, 2023) “On-Demand Microtransit Can’t Escape This Big Problem,” Bloomberg, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-12-19/the-inflexible-problem-with-flexible-microtransit?utm_source=website&utm_medium=share&utm_campaign=copy [Last accessed: 12/22/2023]
To quote from the article:
“Fixed-route service on large buses also offers the economies of scale that microtransit lacks. As long as empty bus seats are available, each new rider brings new revenue to the transit agency while incurring minimal added costs, thereby reducing the subsidy required for each trip. Public dollars can then be reallocated to expand service, which will make transit more useful, thus attracting more riders — and the virtuous cycle continues.
For microtransit, that flywheel effect is missing; the cost of service keeps rising as more people use it. “It would be great to have anywhere-to-anywhere connectivity for the price of transit,” said Goldwyn. ”But it’s just not possible.””
I think this article also touches on motorcycle taxis though perhaps there are also differences between the western and Asian contexts for micro mobility. Surely though, such transport modes cannot approximate transit capacities and require so many more vehicles (e.g., motorcycles) that probably means more chaos and compromised safety along our roads.
–
29th Annual Conference of the TSSP
The Transportation Science Society of the Philippines (TSSP) held its 29th Annual Conference today, December 7, 2023. Following is the program for the conference, which featured a panel discussion in the morning and technical sessions in the afternoon.

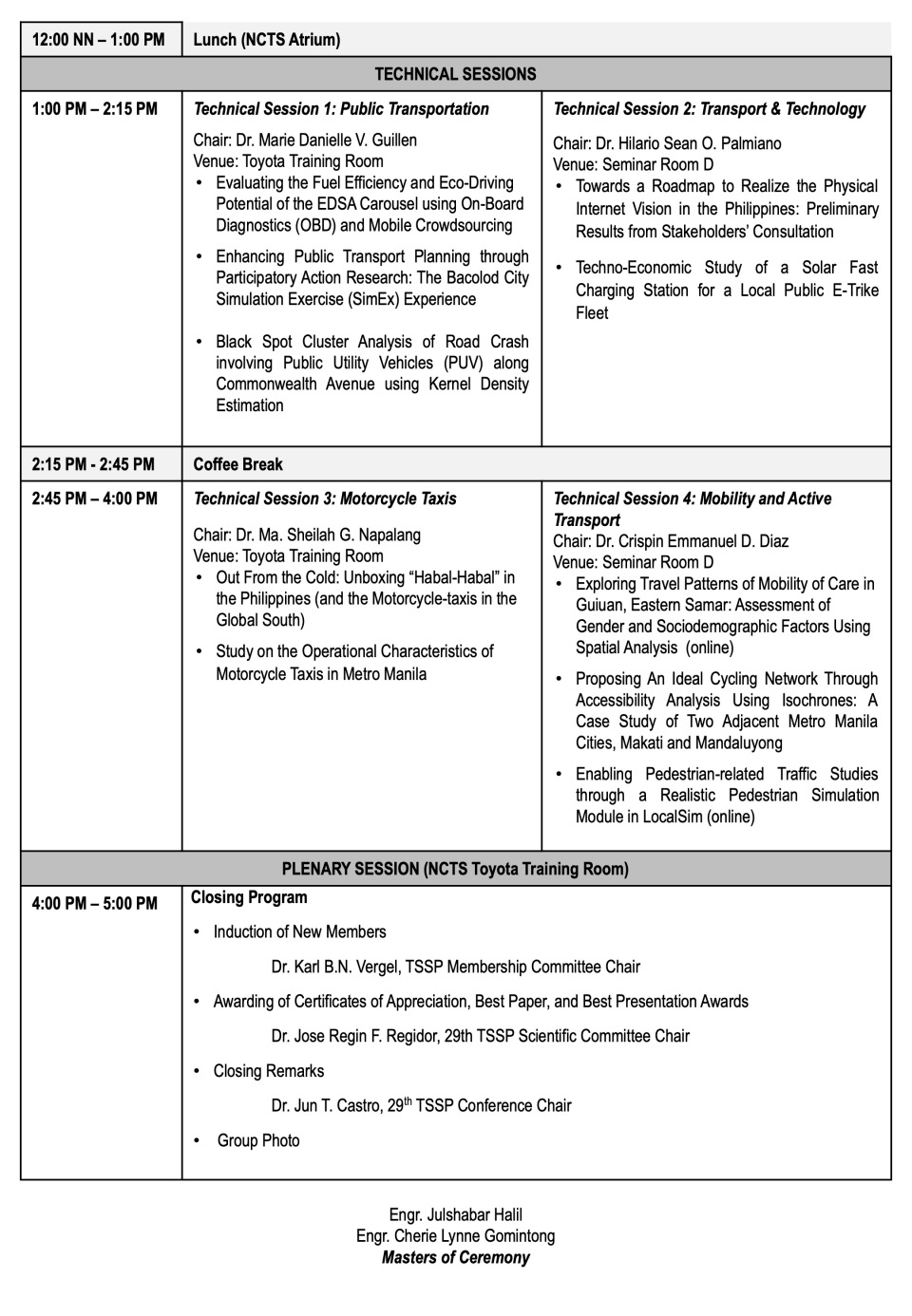
This was the first mainly face-to-face or in-person conference for the society since 2019. Previously, the conferences were online. As reported in the concluding part of the program, there were 84 participants who showed up at the venue while there were 30+ participants who were online via Zoom.
There were a couple of awards at the conference. These were the Best Paper Award and the Best Presentation Award. The Best Paper Award, based on the scores garnered from the blind review of the papers went to:
Maria Belen Vasquez and Jun T. Castro of UP Diliman for their paper entitled “Exploring Travel Patterns of Mobility of Care in Guiuan, Eastern Samar: Assessment of Gender and Sociodemographic Factors Using Spatial Analysis”
There was a tie for the Best Presentation Award. The two were Ms. Vasquez for the presentation of the paper on the Mobility of Care in Eastern Samar, and Mr. Erris Sancianco for the presentation of a paper he co-authored with Noriel Christopher Tiglao, Niki Jon Tolentino, Gillian Kate Hidalgo, Mary Joy Leanda, and Lester Jay Ollero entitled “Evaluating the Fuel Efficiency and Eco-Driving Potential of the EDSA Carousel using On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) and Mobile Crowdsourcing“. These papers will likely find their way to the Philippine Transportation Journal’s next issue.
Though it was not announced, a likely venue for the next conference will be Vigan, Ilocos Sur in the Northern Philippines. The likely host will be the University of Northern Philippines, the premier state university in that province. Previously and most recently, the conference was held in Cebu City (hosted by the University of San Jose-Recoletos) in 2019 and before that in Cagayan De Oro City (hosted by Xavier University) in 2018. TSSP was already organizing the 2020 conference when the pandemic struck and the country went on a lockdown. That conference was supposed to have been held in Baguio City in Benguet, and to be hosted by St. Louis University.
More information on the conference may soon be found at the TSSP’s official website: https://ncts.upd.edu.ph/tssp/
–
Article share: Drought and the Panama Canal
Here’s a quick share of an article on how a drought is affecting operations of the Panama Canal:
Eavis, P. (November 1, 2023) “Drought Saps the Panama Canal, Disrupting Global Trade,” Wired, https://www.nytimes.com/2023/11/01/business/economy/panama-canal-drought-shipping.html?unlocked_article_code=1.7kw.9CNJ.NKhQS8RCMh9h&smid=url-share [Last accessed: 11/3/2023]
From the article:
“But a drought has left the canal without enough water, which is used to raise and lower ships, forcing officials to slash the number of vessels they allow through. That has created expensive headaches for shipping companies and raised difficult questions about water use in Panama. The passage of one ship is estimated to consume as much water as half a million Panamanians use in one day…
Without a new water source, the canal could lose significant amounts of business. Other ocean routes are, of course, longer and more expensive, but they are less likely to have unpredictable delays. One alternative is to transport goods between Asia and United States through the Suez Canal to the East Coast and Gulf Coast. Another is to ship goods from Asia to the West Coast ports — and then transport them overland by train or truck…”
I suddenly remembered the current work along the Marikina River. The government is supposed to be working towards making the river navigable for the Pasig River Ferry to extend operations there. However, the depth of the river prevents regular, reliable operations. I wonder if the current project that includes flood control, riverside roads and erosion control components also will lead to a navigable depth for the river for most if not the whole year.
–
Reference share – study on transport equity
Here is a quick share of a study report on equity in public transportation from the Mineta Transport Institute:
Defining and Equity in Public Transportation, https://transweb.sjsu.edu/research/2100-Public-Transit-Equity-Metrics-Measurement
Perhaps income, physical ability/disability, age and gender are the more applicable aspects of equity in our case. However, the concepts and methodology in the report may still be applicable and can be customized or contextualized for the Philippine setting.
–
