Home » EST (Page 4)
Category Archives: EST
On the impact of bike lanes on motor vehicle traffic
With the news that bike lanes will be removed along major roads including, most recently, I share some findings from the US about a decrease in traffic speeds when there are protected bike lanes. The decrease in speeds are associated with a reduction in road crashes, ergo safer streets.
McPherson, K. (June 3, 2024) “Traffic Speeds Decrease When Bike Lane is Present,” Rutgers.edu, https://www.rutgers.edu/news/traffic-speeds-decrease-when-bike-lane-present [Last accessed: 6/8/2024]
To quote from the article:
“They found that the presence of the delineated bike lane made a difference: a 28 percent reduction in average maximum speeds and a 21 percent decrease in average speeds for vehicles turning right. For those heading straight and not turning, a smaller speed reduction of 8 percent was observed. In addition, drivers moving at a perpendicular angle to the bike lane did not slow down.
Marking the bike lanes with cones as a clearly delineated space was more effective at reducing speed than a painted-only bike lane. The painted-only bike lane was associated with a smaller speed reduction of between 11 percent and 15 percent, but only for drivers turning right.
Younes hypothesized that drivers slow down when they see a bike lane marked with the cones because the driving lane is narrower and requires more concentration, and it’s easier to notice cones or planters or some other space delineator than it is to spot painted lines on the road surface.”
Of course, one major element that was probably not considered in their studies is the presence and behavior of motorcycle riders. Motorcycles here frequently enter and use bike lanes whether protected or not. Often they crowd out bicycle users leading to situations where riders of motorized and non-motorized 2-wheelers come into conflict. Still, it would be nice to have a study to determine not just whether there are similar outcomes here but to what extent as well as how motorcycles figure in the study.
–
Pave paradise
With the arrival of rains, many would probably forget about the recent heat wave we experienced. Those days were definitely record-breaking in as far as temperatures and heat indices were concerned. It was so hot that many schools had to revert to online or hybrid modes. Many people were complaining and as usual, the loss or lack of trees were mentioned in conversations or exchanges about how trees and other foliage could have helped cool the earth. The problem is that we have not learned our lesson and continue removing trees particularly those that need not be removed or cut down. In the name of road widening, which appears to be a key performance indicator for the DPWH, trees have been removed along national roads. This led to the elimination of what used to be shaded roads (i.e., canopies provided by trees), and gave way to now very exposed and open spaces.


The very same trees providing us with oxygen and shade, and contributing to cooler temperatures are also the ones helping reduce flooding. Denuded mountains and hills easily have their soils saturated leading to landslides that often are destructive and murderous. While it seems cliche to state that government should lead in ensuring we have more trees, it is a truth and we are in search of champions in government to inspire us to work together for more trees for our future.
–
Another roadblock for active transport?
The Metro Manila Development Authority (MMDA) recently released what they claim to be their counts of bicycle traffic along major roads in Metro Manila from 2020 to 2023.
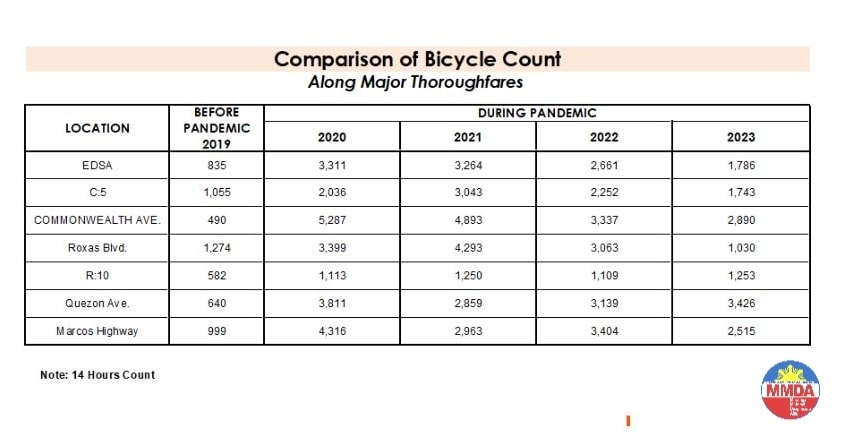
These are supposed to be official data as it is issued by the government agency in-charge of traffic management for Metro Manila roads (aside from its other functions and roles). What are not stated, and are actually very important details, are the locations of the counts and when the counts were conducted. The Traffic Engineering Center (TEC) that was under the DPWH and currently with the MMDA used to publish traffic volume maps for major roads in Metro Manila. So along EDSA, for example, the volume per section are shown on the map. The same for other major roads like Commonwealth, Quezon Avenue and SLEX. The thicker lines mean higher volumes along those sections, and vice versa. However, they did not consciously count bicycles (only motor vehicles) and perhaps MMDA only started counting during the pandemic (i.e., 2020). So there is no one value to represent a road. And counts vary over time of day, day of the week and even throughout the year (i.e., monthly variations).
There were many reactions to the MMDA’s posting of the data and most were critical and even derided the agency for what to them appeared to be inaccurate data. The problem is that it seems there are no other counts that can validate and perhaps refute the MMDA data. Previous bike counts were not conducted according to how the MMDA and DPWH count vehicles. That is, counts are typically done over a 14 or 16-hour period and ideally on several days in a year. Expansion and conversion factors are applied based on established stations along major roads that are supposed to have more frequent if not continuous counts. This methodology is how Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) is computed. Call it car-centric if you like but the methodology is very much applicable to bicycles as well. Peak hour counts for bikes are not enough and the peak hour factor for motor vehicles does not apply to bicycles (if this is to be used to expand/convert peak volumes to daily values). In fact, if you go into the math, there should be a peak hour factor for each type of vehicle considering each vehicle’s volume will vary differently over time. So yes, the solution here is to conduct bicycle counts according to how MMDA or DPWH counts vehicles and these should be done along several stations along major roads (e.g., those in the table above) to validate the MMDA counts.
More on this topic in the next post!
–
On non-roadway traffic deaths and incidents
I found this interesting article about non-roadway crashes or incidents that may cause deaths. These are often recorded in buildings including parking lots or facilities but are not generally collected and reported by governments as part of road crash data.
Wilson, K. (April 18, 2024) “Why Does the Vision Zero Movement Stop At the Edge of the Road?,” Streetsblog USA, https://usa.streetsblog.org/2024/04/18/why-does-the-vision-zero-movement-stop-at-the-edge-of-the-road [Last accessed: 4/28/2024]
From the article:
“According to the latest report from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, a shocking 3,990 people died in car crashes that occurred outside of the traditional transportation space in 2021, the last year for which data is available. One-quarter of those people were outside vehicles, including, pedestrians, cyclists, wheelchair users, and even children simply wishing their parents goodbye before they were accidentally run over by the caregivers who loved them most; all lost their lives after they were struck by drivers on private property, like parking lots, driveways, drive-thrus, and private roads.”
These crashes very likely contribute to under-reporting. One wonders, for example, how many incidents occur in mall parking lots, schools and subdivisions. Recall the incident in Ateneo years ago when a child got ran over and killed as students were being dropped off in the morning. Surely there are other incidents though not involving deaths, and these need to be recorded among traffic incidents. The deaths need to be included in the reports. These are important information to complete the picture of road traffic safety in any country including the Philippines.
–
Article share: on making more affordable neighborhoods
I’ve been commenting about how transportation cannot be isolated and the need to relate it to other factors such as housing or home location choice. The latter though is also affected by other factors as well that affect the affordability of homes near the city centers or CBDs where workplaces and schools are located. The result of course is sprawl or the encouragement of sprawl. Private companies take advantage of this or contribute to this ‘encouragement’ by developing land farther away from the center. Thus, for Metro Manila’s case, many people reside in the peripheral provinces of Bulacan, Rizal, Laguna and Cavite. There are even those who choose to reside in Pampanga, Bataan and Batangas.
Kayatekin, C.S. and Sanmiguel, L.U. (April 16, 2024) ” ‘Urban form’ and the housing crisis: can streets and buildings make a neighborhood more affordable?” The Conversation, https://theconversation.com/urban-form-and-the-housing-crisis-can-streets-and-buildings-make-a-neighbourhood-more-affordable-224108 [Last accessed: 4/23/2024]
Quoting from the article:
“Our main finding was that the bottom-up districts we looked at had, overall, more small-scale apartments. The reason is simple: they had more small-scale buildings, built on small-scale plots. Once divided into apartments, this produces small apartments – homes in the bottom-up areas were 10% to 23.1% smaller than their top-down counterparts. This also made their real estate markets for small homes more competitive, and therefore more affordable.
However, our study showed there is nothing inherently magical about bottom-up areas. Their more intricate housing stock has little to do with the layout of streets and blocks, and a lot to do with how that land is built upon.
Plot size appears to be the deciding factor: the districts with greater numbers of small buildings built on small plots supported a denser and more affordable housing stock, regardless of whether they were top-down or bottom-up.
Older bottom-up areas seem to naturally lend themselves to having more small-scale plots. This is likely due to the incremental development of these areas, and the complex land ownership patterns that developed as a result. However, there is no reason why a top-down area cannot be designed to replicate these characteristics.”
–
When Driving Isn’t an Option: Steering Away From Car Dependency
Here is another quick share of an article from Planetizen. The article relates about people who cannot drive so driving for them is not an option:
Source: When Driving Isn’t an Option: Steering Away From Car Dependency
Quoting from the article:
“Zivarts shows that it is critical to include people who can’t drive in transportation planning decisions. She outlines steps that organizations can take to include and promote leadership of those who are most impacted—and too often excluded—by transportation systems designed by and run by people who can drive. “
There are actually many who can drive and who would like not to drive but then opt to drive because of limited and inconvenient or uncomfortable options. I think government agencies and local government units are supposed to work on this but like people who try to ‘solve’ traffic by isolating it from other factors such as housing, they ultimately gain little ground if not fail. It doesn’t help that the decision makers such as government officials and politicians drive or are driven. Of course, there is still such a thing as empathy so let’s not discount those who do use cars for their commutes but also work hard to improve transportation. It’s just that such people are rare these days and may not be in a position to move things to enable significant improvements to the transportation system.
–
Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here is a quick share of another very informative article that discusses the importance of proximity and more dense development in order to reduce car dependence.
Source: Planning for Accessibility: Proximity is More Important than Mobility
Here are some excerpts from the article:
“This shows that proximity is much more important than mobility in providing accessibility: location, location, location. For the last century, our transportation planning practices have contradicted this principle. Transportation agencies built urban highways that destroyed and degraded accessible and multimodal neighborhoods to benefit suburban motorists. This was racist and classist, but the mechanism was the way that transportation planners valued increased traffic speeds, measured as travel time savings, while ignoring the loss of accessibility imposed on urban neighborhood residents.
Of course, many other factors affect people’s transportation and neighborhood preferences. Some people need their cars for work or after-work activities, and not everybody can bicycle or use transit even if it is available. However, surveys such as the National Association of Realtor’s National Community Preference Survey indicate that many people would prefer living in more compact, walkable neighborhoods than they currently do but cannot due to a lack of supply.”
Such articles are a must read for those who want to understand why government needs to invest in land at or near the CBDs, and develop that land so people will not need to reside far from their workplaces and schools. Truly, there are many other factors affecting transport preferences or mode choice. Housing is one such factor that we continue to treat separately from transport. It is very (prohibitively) expensive to buy or rent in the city particularly in or near the CBDs. The result is people opting to purchase or rent homes in the suburbs. It doesn’t help that developers are also actively promoting subdivisions there and therefore are contributing to sprawl that puts so much pressure on transportation systems.
–
30th Conference of the Transportation Science Society of the Philippines
I am sharing here the First Call for Papers for the 30th Annual Conference of the Transportation Science Society of the Philippines (TSSP). The conference will be held in Iloilo City almost to the day of the last time it was held there in Sept. 12, 2014.

Information on past conferences may be found here: https://ncts.upd.edu.ph/tssp/conferences
–
Article share: The Benefits of Trees
Here is a quick sharing of this article on the benefits of trees. I thought such articles are always timely and relevant especially if you frame this in the context of road or highway development as well as the complete streets concept that is currently being promoted to improve transport conditions including road safety.
Source: The Benefits of Trees
Article share: on subsidies to public transportation
Here’s a nice article that presents arguments for subsidies to support transit or public transportation:
Wilson, K. (February 5, 2024) “Study: Subsidizing Transit Actually Makes It More Efficient,” Streets Blog USA, https://usa.streetsblog.org/2024/02/05/study-subsidizing-transit-actually-makes-it-more-efficient [Last accessed: 2/18/2024]
Subsidies to public transportation can be quite tricky and may require quite a balancing act. There seems to be few options outside of the straightforward subsidies national and local governments in the Philippines provide. Rail transit, for example, is heavily subsidized but these are rare for road-based public transportation. The concept of service contracting has been considered but it also has a few variations. While there seems to have been a proof of concept tested during the pandemic, it required so much funds that government apparently lost interest (i.e., the funds were also needed by other sectors). Local governments meanwhile, or at least those that had resources, decided to operate their own public transport (e.g., Quezon City bus).
To quote from the article:
“Newmark’s study doesn’t definitively determine why, exactly, high subsidies seem to correlate with better efficiency and transit agencies collecting more fares, but he has some theories. Some systems, he says, use subsidies to increase service frequency or install dedicated lanes to speed routes up along heavily-utilized corridors — and riders are responding, predictably, by showing up in droves. (Route expansion can help, too, he said, but only if agencies expand service to places “where there’s actual demand.”) Others use subsidies to keep ticket prices low, but not to eliminate fares outright, which Newmark argues is a smart move.
“People value stuff they pay for, and they pay for stuff they value,” Newmark added. “An underlying point in this paper is that transit offers something [valuable], and it’s worth trying to capture that value, whether through fares or in other ways.”
If transit networks and the taxpayers who support them can get that recipe right, it could create a virtuous cycle.
“If people see the benefits [of subsidies], that may make them more willing to invest [their taxpayer dollars],” he adds. “Good transit leads to a real social movement for more subsidies.” “
What do you think about subsidies to public transport in the Philippine setting? Of course, we are referring to ‘formal’ public transportation here. There are many ‘informal’ or paratransit modes like tricycles and non-motorized pedicabs. There are also motorcycle taxis providing services or filling in the gaps in transport services.
–
