Home » Mode Share (Page 2)
Category Archives: Mode Share
First impressions of In Drive
There’s another TNVS service operating and competing with Grab. I heard about In-Drive from friends who regularly take Grab when they are in a hurry and opt out of their usual public transport options. They relate that In-Drive was cheaper than Grab based on their most recent bookings. They also said it was easy to book a ride with In-Drive.
And so I downloaded the app and finally had an opportunity to try them as I traveled between UP Diliman and Ortigas Center. I was able to book a ride immediately and it was less expensive compared to Grab. But that was just one booking so I had to try it another time. On my return trip, the same happened and I was able to get the same result with a cheaper booking than Grab.
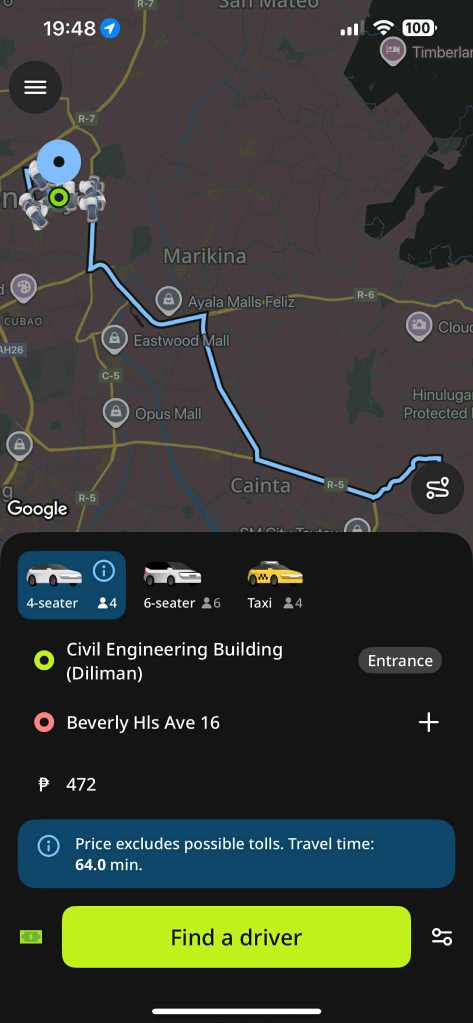
One time I had to travel home from my office in UP after my evening class, I decided to try this again. Here are the screenshots for my evening ride. The first image is for Grab and the second for In Drive. The routes indicated in the maps are the same. Noticeably different are the estimated travel times (73 minutes for Grab vs. 64 minutes for In Drive) and fares (at least 556 pesos for Grab vs. 472 pesos for In Drive). The choice here was easy – In Drive.
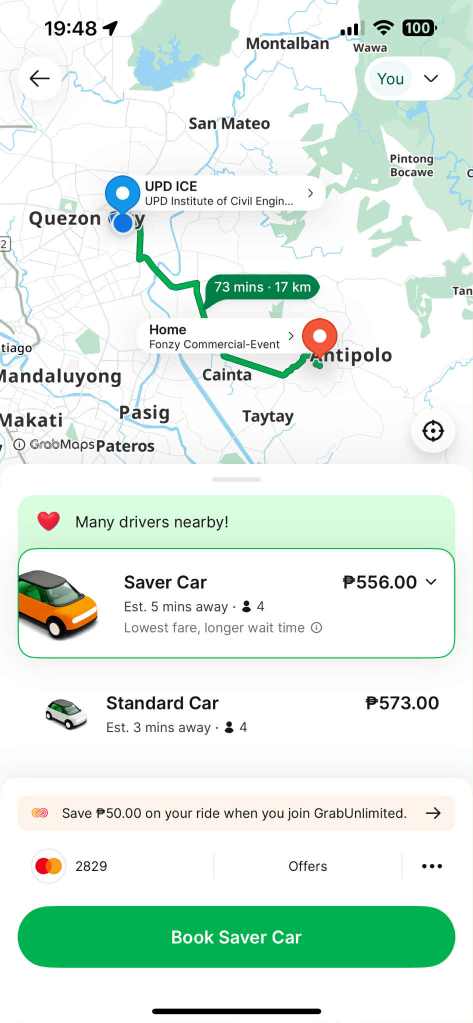
My experiences so far indicate that In Drive was indeed cheaper than Grab. For the last example, it also indicated a shorter travel time. But that’s just me and a few bookings. It is worth studying or exploring further if indeed In Drive, in general, provides for less expensive travel. Other circumstances or conditions can be considered including the origins and destinations for the bookings, the time of day or day of the week, and so on. These are necessary to really have an objective and conclusive comparison of the two.
There’s another option that’s been getting some buzz recently among my friends and students. A taxi company with a full electric car fleet is also now available and competing with the TNVS companies. I will write about Green GSM very soon!
–
Traffic congestion along EDSA
I’ve taken some photos of EDSA traffic as well as the EDSA Carousel buses. Here are the more recent EDSA photos I took as I traveled from Makati to Quezon City after serving as a panelist in the Energy Transitions Dialogue last Wednesday.
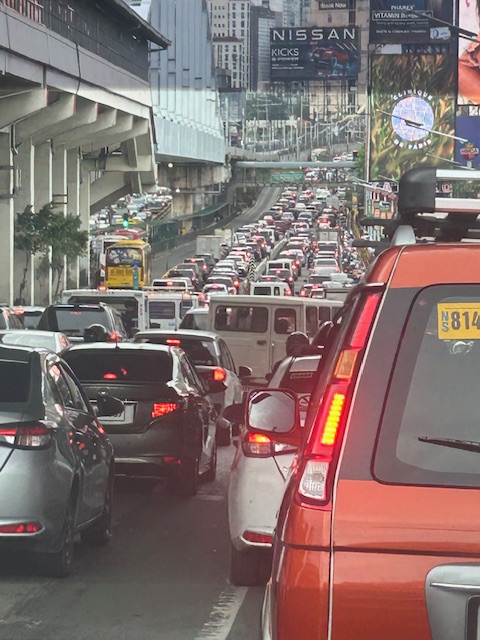 I took this photo as we passed Guadalupe. I like this in the sense that it shows the clear ROW for the EDSA Carousel buses. One wonders why most of these motorists would prefer to drive their vehicles rather than take the bus or the MRT.
I took this photo as we passed Guadalupe. I like this in the sense that it shows the clear ROW for the EDSA Carousel buses. One wonders why most of these motorists would prefer to drive their vehicles rather than take the bus or the MRT.
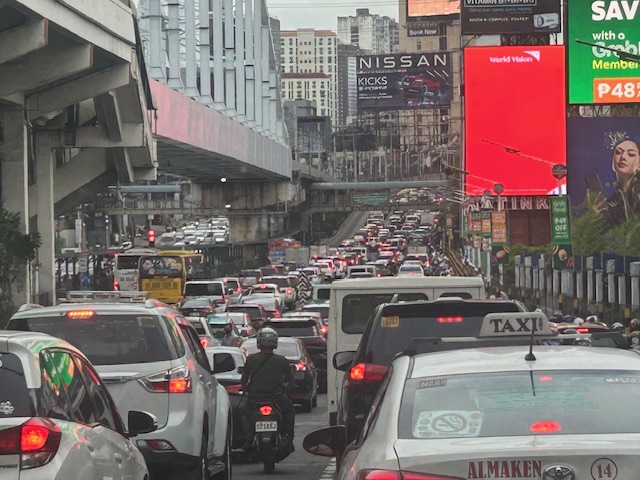 You can see in the photo that EDSA’s northbound side is clogged as far as the eye could see. If you check the image under the MRT bridge, it shows the southbound side was also congested. These photos were taken around 4 PM so this was still an hour before most people would be going home from work.
You can see in the photo that EDSA’s northbound side is clogged as far as the eye could see. If you check the image under the MRT bridge, it shows the southbound side was also congested. These photos were taken around 4 PM so this was still an hour before most people would be going home from work.
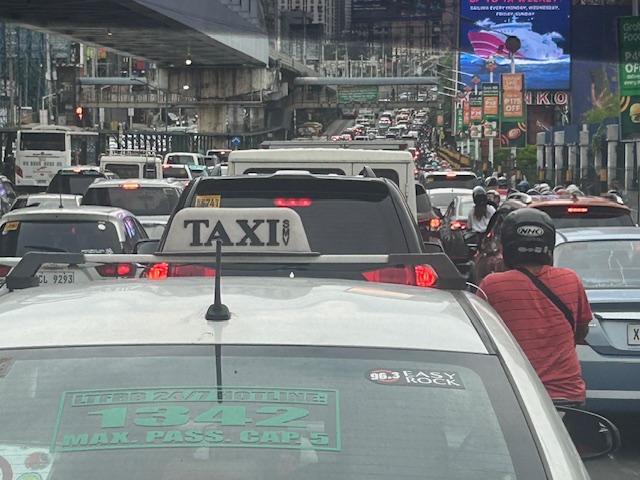 I mentioned in my comments at the panel that one consequence of giving number coding exemption to electric and hybrid vehicles is that this further diminishes the effectiveness (is it still effective?) of the MMDA’s number coding scheme. I don’t have the stats of how many EV’s and hybrids are registered and running in Metro Manila. Those numbers combined with actual counts will tell us how they are impacting traffic. That would be a nice topic for a paper. 🙂
I mentioned in my comments at the panel that one consequence of giving number coding exemption to electric and hybrid vehicles is that this further diminishes the effectiveness (is it still effective?) of the MMDA’s number coding scheme. I don’t have the stats of how many EV’s and hybrids are registered and running in Metro Manila. Those numbers combined with actual counts will tell us how they are impacting traffic. That would be a nice topic for a paper. 🙂
The photos pretty much describe the transport situation in Metro Manila. Many of our major cities will be heading this way unless they improve their public transportation fast. If they do, then public transport mode share will be sustained if not increased. Metro Manila’s is already being eroded by inefficient public transport, motorcycles (including taxis) and perhaps unintentionally, electric and hybrid vehicles.
–
Competition for Grab?
Friends have been talking about the two new options that they say should rival and compete with Grab. These are another ride hail company and, interestingly, a taxi company. That ride hail company is In Drive and the taxi company is Green GSM.
 Green GSM vehicle dashboard showing the taxi meter details
Green GSM vehicle dashboard showing the taxi meter details
The observation and consensus are that either is cheaper than Grab. My personal experience is that they are cheaper than Grab and substantially so. What does this mean? Probably that more people will eventually discover and experience the same and Grab’s ridership will decline. By how much? We don’t know that yet. What we know is that Grab’s most significant competition now are the motorcycle taxis like Angkas and Joyride. Move It is Grab’s response to the other two after it was prevented by government to compete directly with the two. More details in future posts this September.
–
Is it possible to have zero traffic deaths in a year?
Is it possible to have zero traffic deaths in a year? Is it even probable? As it turns out, yes. Here’s an article on what Helsinki did in order to make this a reality:
Andrei, M. (August 1, 2025) “Helsinki went a full year without a traffic death. How did they do it?” ZME Science, https://www.zmescience.com/science/news-science/helsinki-went-a-full-year-without-a-traffic-death-how-did-they-do-it/ [Last accessed: 8/19/2025]
To quote from the article:
“A lot of factors contributed to this, but speed limits are one of the most important,” said Roni Utriainen, a traffic engineer with the city’s Urban Environment Division.
More than half of Helsinki’s streets have a speed limit of 30 km/h (approximately 20 mph). Half a century ago, the city barely had half of its area with a 50 km/h limit (30 mph). They gradually worked to reduce the speed limit, especially around schools and kindergartens.
Smarter street design also played a key role. Pedestrian and cycling infrastructure was prioritized for upgrades in recent years. More and more people started using public transit or bikes, or just walking. Substantial investments also made public transit more efficient and reliable.“Public transport in Helsinki is excellent, which reduces car use, and with it, the number of serious accidents,” Utriainen noted.
Another key component was bringing the police on board. Helsinki introduced automated traffic cameras and enforcement systems, which also helped bring down reckless driving.”
An aerial view of the PNR’s rail revival
I would just like to share a few photos I took while our plane was turning towards our Bicol destination upon take off from NAIA.
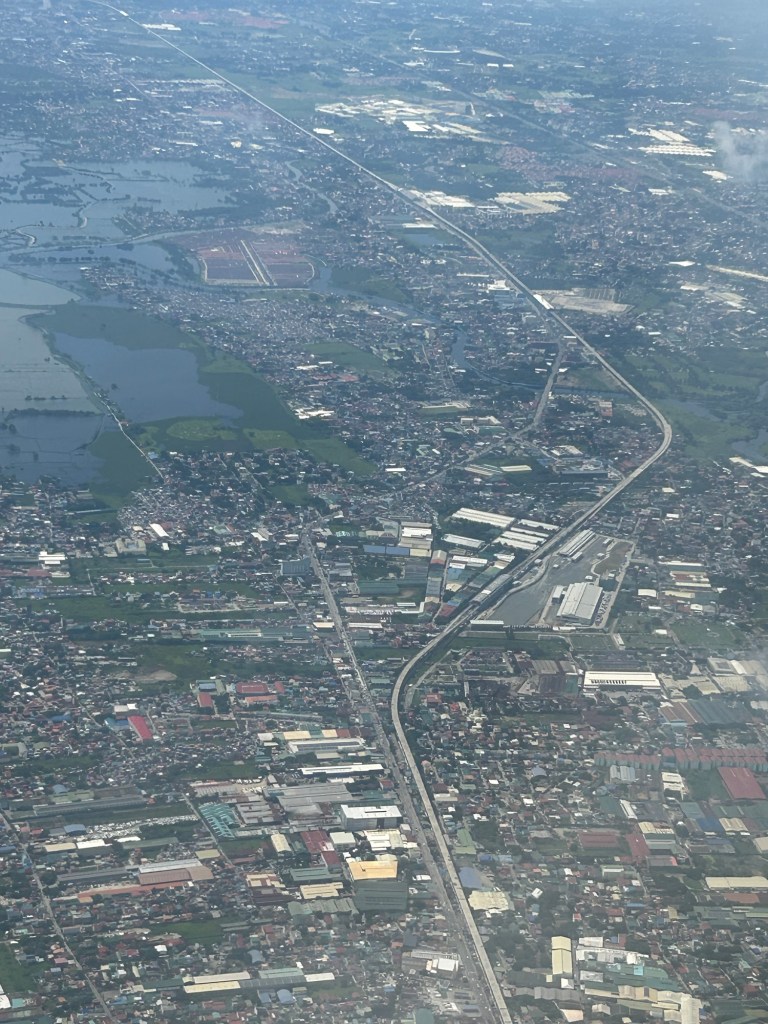
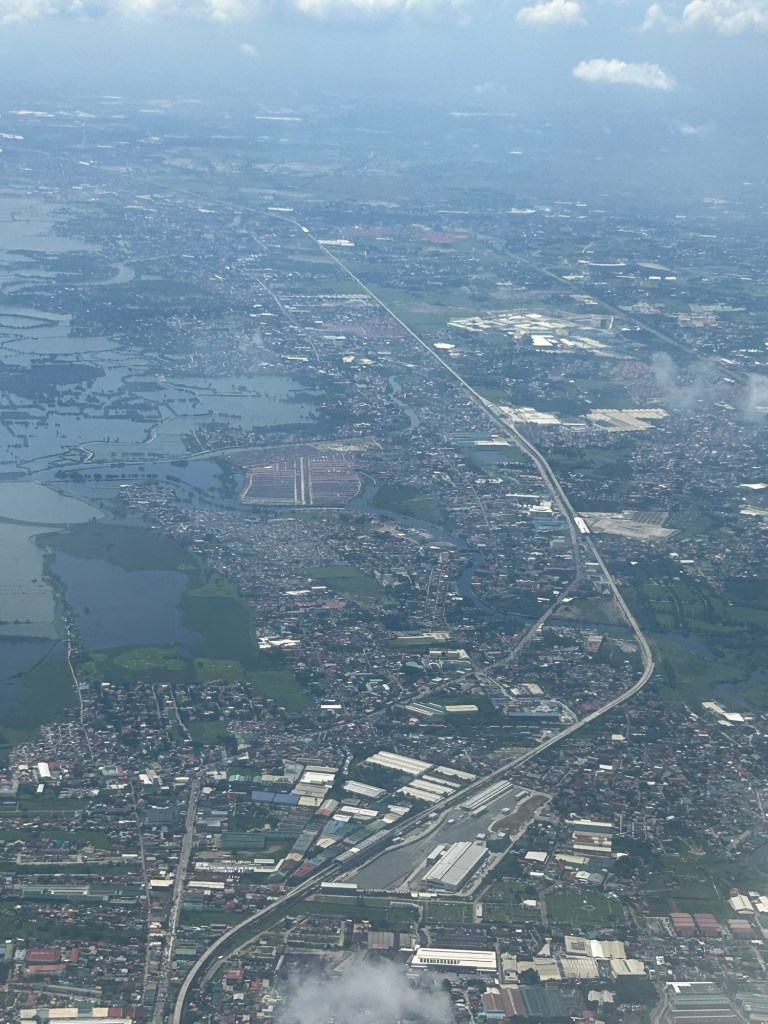
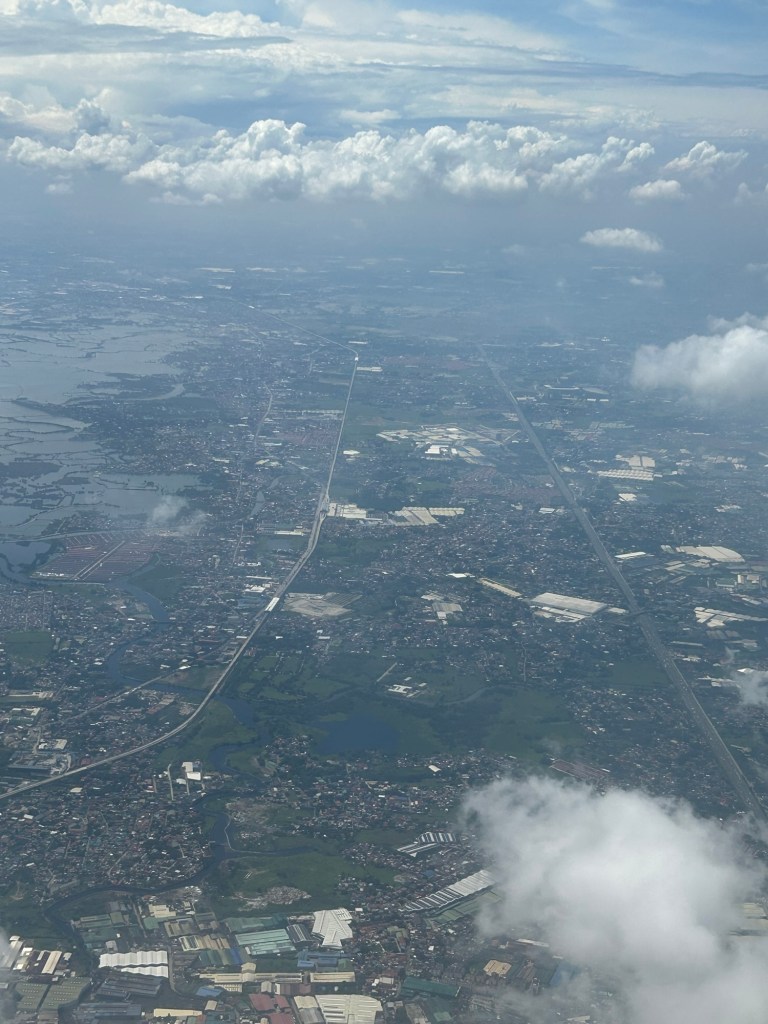
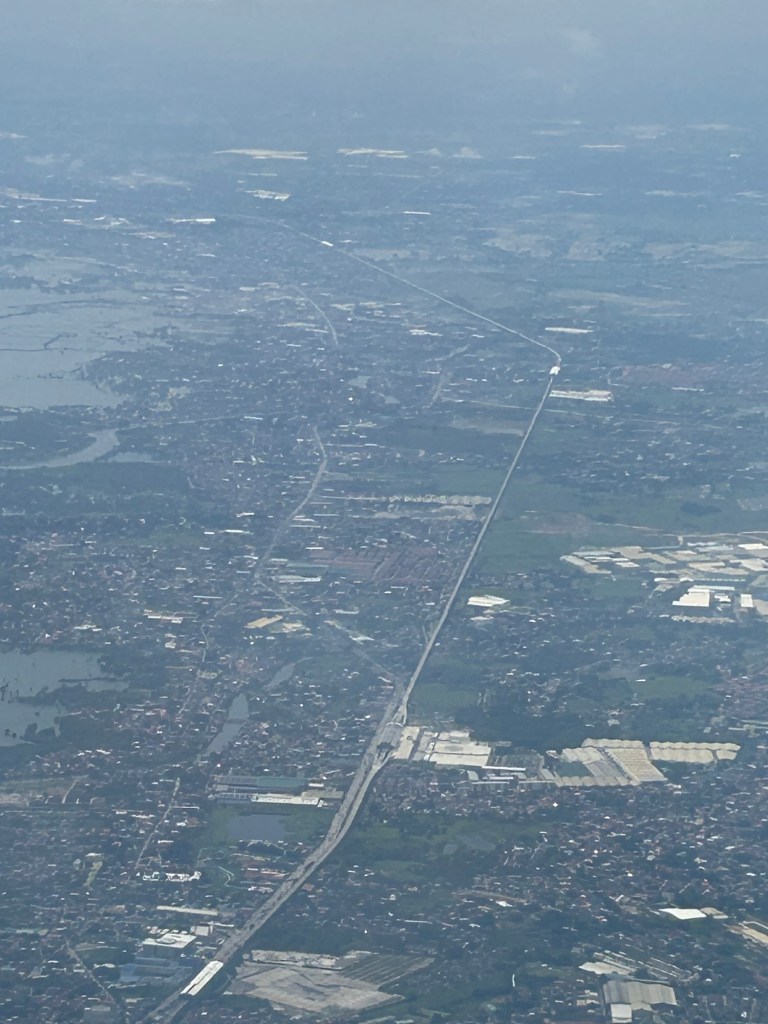




I will again pose the following questions to my readers: will the NSCR become the game changer it’s supposed to be for both long distance travel and commuting (super commuting for some cases)? Will it decongest McArthur Highway and NLEX? Will there be a significant shift from car use to rail? Or will those taking road-based public transport be the ones mainly shifting to rail?
–
Is there really a shortage of public transportation in Metro Manila? – Part 1 – Introduction
I will be doing a series of articles here on public transportation. More specifically, I will try to answer the question in the main title of the series – Is there really a shortage of public transportation in Metro Manila?
The quick answer probably is “yes” but we need to examine this concern from different perspectives and reasons so we can be objective about the “why” part of the shortage. Shortage may mean a real lack in terms of the number of public utility vehicles (PUVs) with approved franchises or perhaps the number actually operating on any given day. These two are actually different because it is possible to have fewer PUVs operating compared to the approved number or to have more PUVs operating than the approved number. The latter means there are “colorum” or illegal operations (i.e., vehicles providing public transport services without franchises).
Among the reasons why there is a perceived shortage of public transportation are as follows:
- Fewer than the number of franchises approved are operating.
- PUVs are not able to make a reasonable turnaround (e.g., due to traffic congestion).
- PUV drivers and operators refusing to operate their vehicles.
- Other factors.
- Any combination of the above including “all of the above.”
I hope I can write about these in a manner that can be easily understood – in layman’s terms.
–
Quick comments on the NCAP
The No Contact Apprehension Policy (NCAP) is finally being implemented in Metro Manila. The results so far has been dramatic in terms of the number of violations recorded and the images being shared so far about how motorists are behaving. Below is one of those photos being shared on social media to which I added some annotations. I will use this later to comment on the NCAP and how we can use the outcomes to assess the transportation situation and determine what interventions can be done. Some are already obvious from the photo – the lack of public transport options lead to people depending on private motor vehicles like cars and motorcycles for their commutes. MRT7 is yet to be operational and road public transport has not been rationalized.
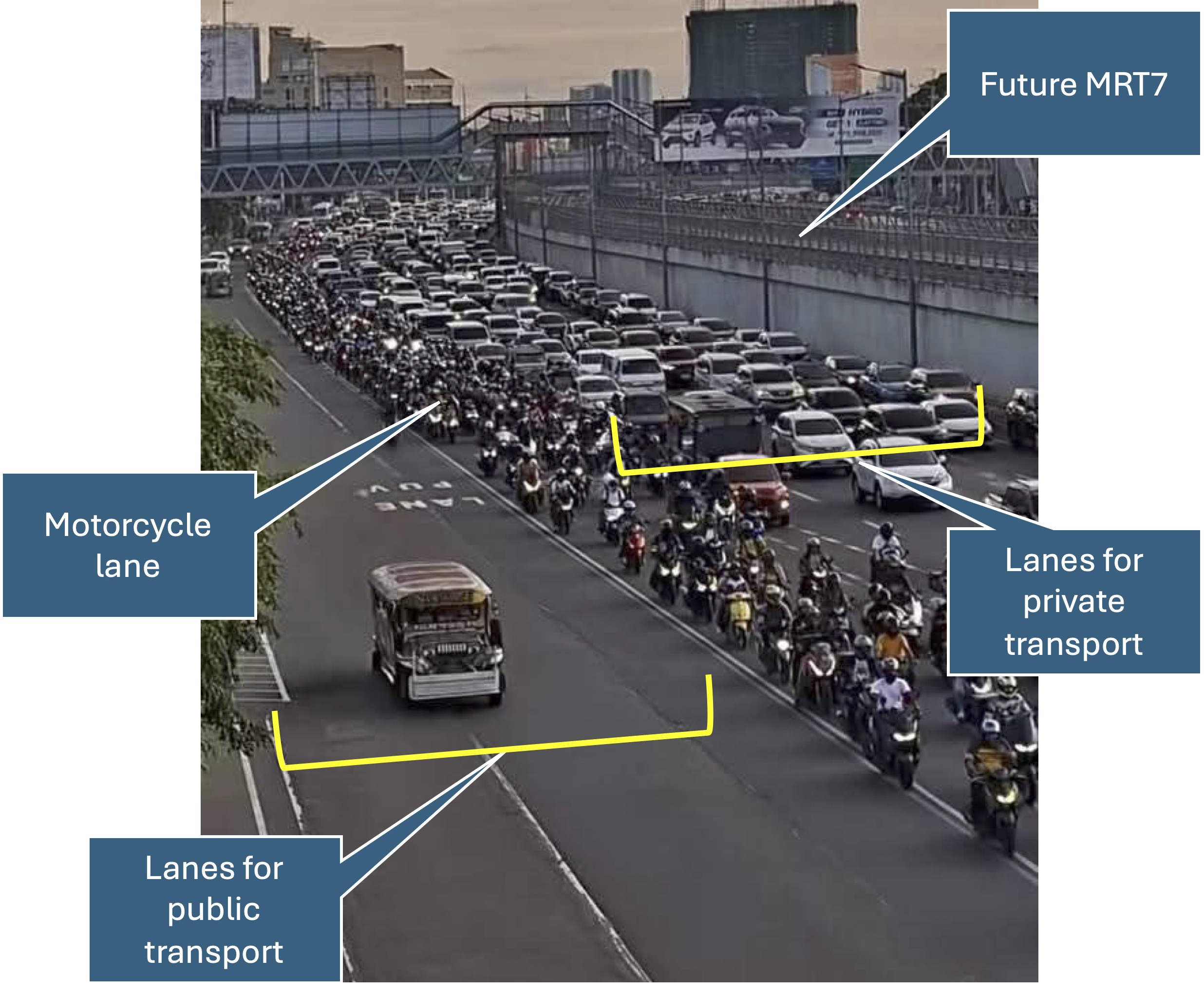
More on this topic soon!
–
Shared article on shared mobility
Here’s is a nice short read on a Sunday about shared mobility. The article is of particular interest to me because it tackles the needs of persons with disabilities, senior citizens and those in low income households.
Seruga, K. (April 14, 2025) “Shared mobility: Making travel easier for all,” Knowable Magazine, https://knowablemagazine.org/content/article/society/2025/increasing-access-to-shared-transportation [Last accessed: 27/04/2025]
“But if you’re disabled or elderly, living in a low-income area or — imagine! — without a smartphone or credit card, using these shared mobility services becomes a lot more difficult. They tend to cluster in more affluent urban areas, and are often inaccessible to people with reduced mobility or those traveling with young children needing child seats. In part because of these factors, users are disproportionately younger, wealthier, able-bodied, white and male.
Shared mobility could be a key part of a more sustainable transportation system. But to be most effective, it needs to include everyone. For-profit shared mobility providers have largely failed to deliver on this, but various initiatives and projects are finding creative solutions to reach underserved communities.
The potential benefits are large. On-demand shared mobility that feeds into well-developed public transportation systems could reduce the number of vehicles in some cities by 90 percent and cut transportation emissions by 50 percent — but only if it largely replaces private car use. “The car has to be a guest, not the main actor,” says Luis Martinez, lead modeler at the International Transport Forum, who coauthored a paper on shared mobility and sustainability in the 2024 Annual Review of Environment and Resources.”
There is a cautionary tale on ‘for-profit’ shared mobility here but a major difference in countries like the Philippines from those in western countries is the presence motorcycle taxis and the surge in the ownership of electric three-wheelers. These have changed the way people travel though their impacts are only now being assessed.
–
“Coding exempt” vehicles and the demise of the coding scheme
I saw this car ahead of me during my commute. I knew this was an electric vehicle and these as well as hybrid ones were given an incentive in Metro Manila. They are “coding exempt” meaning these vehicles can be driven any day and ay hour during the weekdays.
 Are they selling these ‘coding exempt’ accessories or do these go free when you buy these cars?
Are they selling these ‘coding exempt’ accessories or do these go free when you buy these cars?
People ask if the number coding scheme (UVVRP) in Metro Manila is still effective or relevant. Well, the answer is a ‘no’ and that is because over time, people have adjusted to it. Car owners have bought a second, even third vehicle that they call their ‘coding’ vehicle. Others opted to purchase motorcycles. And so that’s what we generally see along most roads in Metro Manila. It didn’t help that hybrid and electric vehicles are given exemption from the coding scheme. Those who can afford to buy yet another vehicle or perhaps replace their conventional ones are already buying these as evident from their increasing presence along our roads. While there is the perceived benefits with less emissions and air pollution, we still lose with congestion and its derivatives. Perhaps we should already have a congestion pricing scheme implemented for Metro Manila like the one in New York City. And proceeds should go to the improvement of public transportation to help arrest the erosion of its mode share in favor of private vehicles.
–
To B(RT) or not to B(RT)?
I kind of expected questions or comments from my ‘students’ after my lecture last Wednesday about “Traffic Congestion.” Among my slides were those featuring solutions to transport and traffic problems. I presented both soft and hard approaches including travel demand management schemes and infrastructure that we should have built decades ago. The uniformed officers who were there had a very simple take on congestion – it’s basically because of a lack of discipline. While theirs may also be valid observations based on their experiences, ‘discipline’ is not the most critical problem that we have especially considering the ever increasing demand for travel. One government official present was very direct in his question about what I thought about the MMDA’s pronouncement that they plan to remove the EDSA Bus Carousel. I thought my reply and the following explanation was clear – it was a wrong move.
The EDSA Bus Carousel is simple. Bus lang sa bus lane (Only buses along the bus lane). Pag may private or pa-VIP, bawal at huli dapat (If there are private vehicles or those who regard themselves as VIPs using the lane, then they should be apprehended. An HOV (high occupancy vehicle) lane is more difficult to implement. Mas pahirapan ang pag monitor and enforce (It is very difficult to monitor and enforce). So this proposal to phase out the EDSA bus lanes don’t make sense from this perspective. In fact, I don’t agree with a couple of more senior transport experts who say that the MRT Line 3 is sufficient and that it hadn’t reached capacity yet. It has but in the time that the carousel has been operational, the carousel had absorbed much of the demand along the corridor. There is also the fact that it will take much time before Line 3 is upgraded. Are the new train sets here? Are the stations designed for these trains and more passengers? If the answers are no, then MRT3 will not have its capacity increased in such a short time. That also means the carousel is very much relevant not just to supplement MRT3 capacity but as a needed alternative mode for commuters.
–