Home » NMT (Page 4)
Category Archives: NMT
Why do we keep widening roads?
I’m just going to share this article here. The article from The NY Times asks a question that has been bugging planners and engineers, particularly those who are in government and perhaps under the agencies like the DPWH, DOTr and NEDA. This also applies to planners, engineers and those from other disciplines involved in transportation infrastructure development and particularly roads or highways.
–
Another definition of the 15-minute city
We begin 2023 with an informative article defining the “15-minute city”. This is actually an entry in Planetizen’s Planopedia, which contains definitions of fundamental concepts in urban planning:
Ionescu, D. (December 2022) “What is a 15-minute City?” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/definition/15-minute-city?utm_source=newswire&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=news-12292022&mc_cid=ee083e2ee7&mc_eid=9ccfe464b1 [Last accessed: 1/1/2023]
I’ve written and shared articles about this concept before. Here are a couple from 2021 where I offered my opinions about the concept as already applied in the Philippines:
https://d0ctrine.com/2021/08/13/on-defining-the-15-minute-city/
https://d0ctrine.com/2021/04/07/didnt-we-already-have-15-minute-cities-and-towns-in-the-philippines/
–
Examples of legislative actions in support of active transport
While the Philippine government and various local government units seem to be reneging on their commitments to support active transport, other countries have been building on their gains during the pandemic. Here are examples of legislations in New York State that will support active transport through funding of complete streets projects and institutional arrangements for representation of transit dependent individual:
The article is about two legislations:
Legislation (S.3897/A.8936-A) Provides Funding for “Complete Streets” Projects Inclusive of a Holistic Approach to Street Design
Legislation (S.3959-B/A.7822-C) Adds Board Seats to NFTA, RGRTA, CDTA, and Central New York Regional Airport Authority Dedicated to a Transit Dependent Individual
We hope to see something like these at least at the local level. Perhaps if LGUs are able to legislate and implement these, there will be more good practice examples that will compel national government to support active transport development. The latter is actually ironic considering that many plans are supposed to spell out the national government’s commitment to active transport. There are still live memorandum orders and department orders supporting and promoting active transport. Are these also being waylaid? That will be tragic for transportation if we didn’t learn or gain anything from the experiences during this pandemic.
–
On the future of bike lanes in Metro Manila and other cities and municipalities in the Philippines
My friends and I were talking about the current buzz about the bike lanes including statements made by certain personalities (influencers, advocates, government officials, etc.) about biking and bike lanes. There were many recent pronouncements of motorcycles being allowed to use bike lanes or the outright removal of bike lanes. We all agreed this was backward and the way forward is to build on the current network and facilities. What we have in our cities and municipalities are not perfect and far from ideal but they are a start and perhaps the foundation for a bikeway network that can eventually make a dent on the car-centric transportation we have.
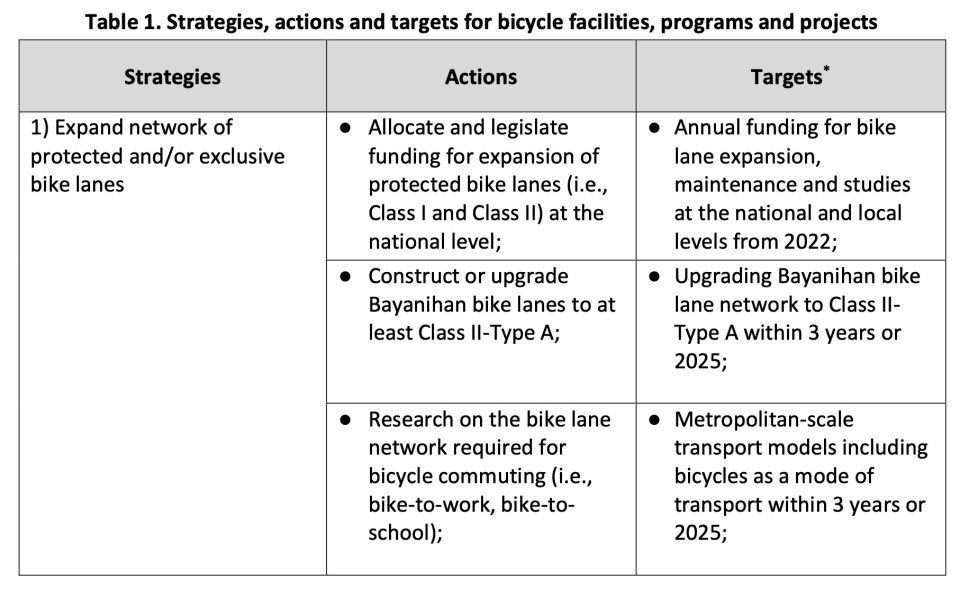
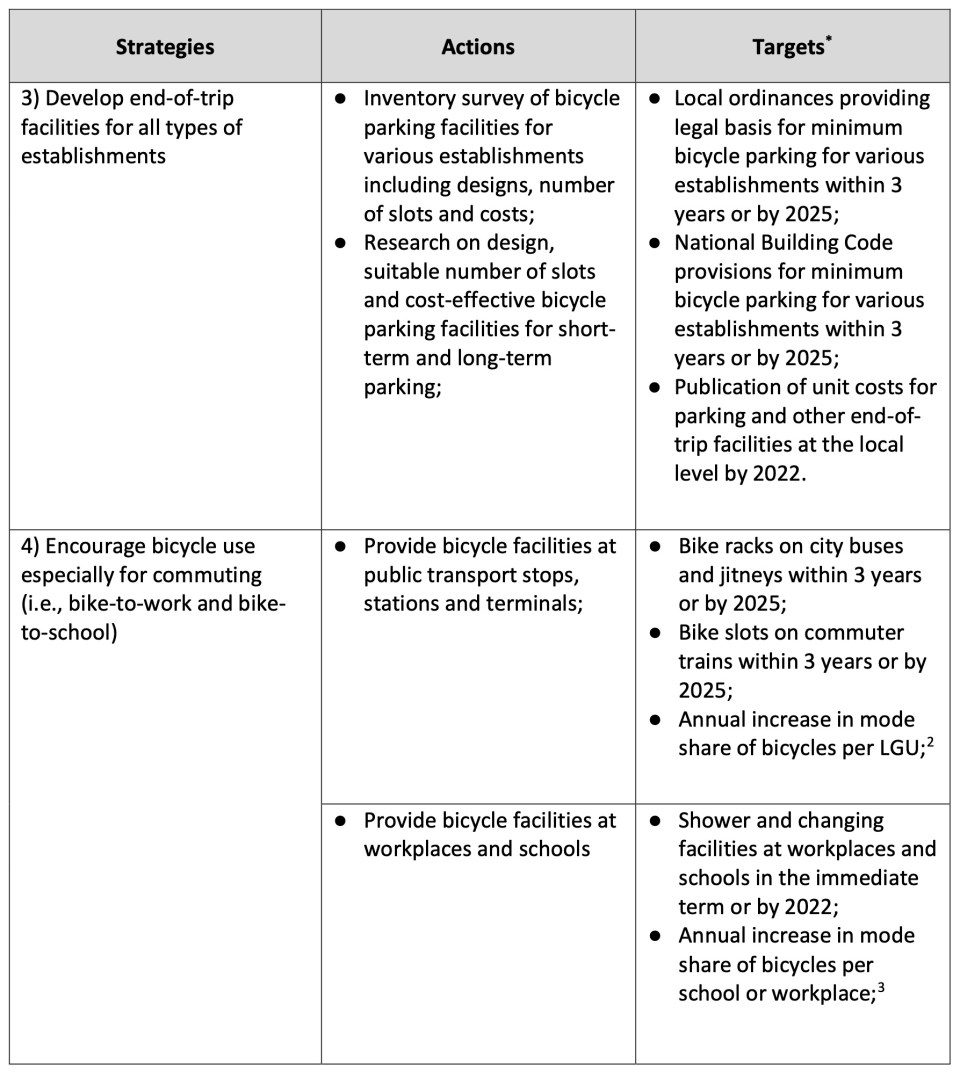
I share below the strategies, actions and targets for bicycle facilities, programs and projects from the Network Planning for the Establishment of Bike Lanes in Metro Manila, Metro Cebu and Metro Davao that was completed middle of 2022. The project is DOTr’s with support from the UNDP. The table is from the Final Report of the project.


A Happy Christmas to all!
–
Shared article: Active and Micro Mobility Modes Can Provide Cost-Effective Emission Reductions–If We Let Them
I’m sharing this article on active and micro mobility modes from Todd Litman, published in Planetizen.com:
Source: Active and Micro Mobility Modes Can Provide Cost-Effective Emission Reductions–If We Let Them
From the article:
“Common Active Transportation Leverage Effects:
–Shorter trips. Shorter active trips often substitutes for longer motorized trips, such as when people choose a local store rather than driving to more distant shops.
–Reduced chauffeuring. Better walking and bicycling conditions reduces the need to chauffeur non-drivers (special trips to transport a passenger). These often require empty backhauls (miles driven with no passenger). As a result, each mile of avoided chauffeuring often reduces two vehicle-miles.
-Increased public transit travel. Since most transit trips include walking and bicycling links, improving these modes supports public transit travel and transit-oriented development.
-Vehicle ownership reductions. Active mode improvements allow some households to reduce their vehicle ownership, which reduces vehicle trip generation, and therefore total vehicle-miles.
-Lower traffic speeds. Active travel improvements often involve traffic speed reductions. This makes non-auto travel more time-competitive with driving and reduces total automobile travel.
-More compact development. Walking and bicycling support more compact, multimodal communities by reducing the amount of land devoted to roadways and parking, and creating more attractive streets.
-Social norms. As active travel increases, these modes become more socially acceptable.
The article is a must read if we are to understand how important active transport and micro mobilities are in the context of today’s transport conundrum. Of course, part of the contextualization and perhaps ‘localization’ on these modes will be related to land use or development. The latter is a big challenge especially for the likes of Metro Manila and other rapidly developing cities in the Philippines where housing in the cities (related to compact development) has become quite expensive and has driven more and more people to live in the suburbs. As I’ve mentioned in previous posts, this has resulted in more pressure to develop transportation systems but infrastructure development cannot play the catch up game given the limited resources for their construction. Meanwhile, services are also behind in terms of quality and requires reforms and rationalizations.
–
On reducing driving and its inherent risks
Ever since the automobile was invented and eventually mass-produced, there has been an increasing risk associated with motor vehicle traffic. Laws, policies and regulations have also been influenced to favor the car rather than people. And so we now have what is termed as a car-oriented and dependent transportation system that seems so difficult to undo as most people appear to be enamored by the car. Owning a car (or even a motorcycle if you want to extend this idea of individual ownership) remains an aspiration to a lot of people.
Here is a link to the compact version of a comprehensive report by Todd Litman that presents and argues for a new paradigm where driving is considered a risk factor. There are data and a table comparing old and new traffic paradigms to help us understand the situation and what needs to be redefined or re-framed in order to achieve our safety targets or vision.
Litman, T. (October 20, 2022) “Driving as a Risk Factor: A New Paradigm,” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/blogs/119287-driving-risk-factor-new-paradigm?utm_source=newswire&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=news-10202022&mc_cid=beacdc2a04&mc_eid=9ccfe464b1 [Last accessed: 10/28/2022]
To quote from the article:
“Safer vehicles, roads, and driving may reduce crashes but achieve few other goals, and sometimes contradict them. Transportation demand management and smart growth policies increase safety in addition to helping to achieve other planning goals, and so can be considered win-win solutions.
More comprehensive safety analysis tends to support social equity goals. Many conventional safety strategies, such as larger vehicles with more passenger protection, and wider roads with fewer intersections, tend to increase walking and bicycling risks. In contrast, lower traffic speeds, TDM, and Smart Growth tend to improve safety, mobility, and accessibility for people who cannot, should not, or prefer not to drive.”
The key takeaway here should be that people should have the option of not driving at all in order to reduce the risks associated with driving as well as reduce congestion. A more comprehensive
–
On making streets safer through woonerfs
One of the new things I learned when I was taking up transportation planning as an undergraduate student in the 1990s was about the woonerf. Our teacher then was a Visiting Professor from the Tokyo Institute of Technology. He introduced to us many concepts in that elective course that paved the way to a number of us proceeding to specialize in transportation. What is a woonerf? Well, here’s a nice article defining the woonerf and providing some examples:
Ionescu, D. (October 6, 2022) “What is a Woonerf?” Planetizen, https://www.planetizen.com/definition/woonerf?utm_source=newswire&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=news-10062022&mc_cid=9d60b3d668&mc_eid=9ccfe464b1 [Last accessed: 10/10/2022]
To quote from the article:
“Translated as “living street,” a woonerf employs strategies like traffic calming devices and low speed limits to force drivers to slow down and safely share street space with pedestrians, cylists, and others, often without raised curbs separating cars and pedestrians. In the Netherlands, where the woonerf originated in the 1960s, motorized traffic within woonerf zones is limited to walking speed…
…A woonerf is not a pedestrianized street, but rather one where multiple users and vehicles co-exist. However, a woonerf can be converted to car-free uses using bollards or other barriers. The woonerf maintains utilitarian uses like loading docks and parking while making the roadway safer and more accessible to non-drivers.”
There should be many applications to the woonerf in the Philippines especially in areas where the dominant land use is residential and through traffic should be discouraged. This is goes well with the complete streets concept that is now being promoted and in fact pre-dates the concept and was well ahead of its time.
–
Bike parking at SM Masinag
With the increasing popularity of cycling, particularly the utilitarian kind (i.e., bike-to-work, bike-to-school, bike-to-shop, etc.), there is also the increasing need to provide facilities for cycling. Aside from the obvious (i.e., bike lanes), there are also what are termed as end-of-trip facilities, the most basic of which are parking. These may be spaces or slots allotted at workplaces, schools, markets, malls, government buildings, churches, etc. for cyclists or bikers to secure their vehicles. Bicycles may also be used as ‘last mile’ modes of transport so bike parking are necessary at transit or train stations. It is heartening to see the big malls like SM and Robinsons provide parking facilities for bicycles. Here are some photos of the bike station at SM City Masinag in Antipolo City.
 End of trip facilities in the Philippines is generally a work in progress. Hopefully, we get to benefit from their provision where they are needed – workplaces, schools, government buildings, commercial establishments, etc.
End of trip facilities in the Philippines is generally a work in progress. Hopefully, we get to benefit from their provision where they are needed – workplaces, schools, government buildings, commercial establishments, etc.
 The bike station at SM Masinag includes this bike repair stand with the basic tools for bike repairs and tire inflation.
The bike station at SM Masinag includes this bike repair stand with the basic tools for bike repairs and tire inflation.
 The bike station is just across from the Line 2 Antipolo Station (what was supposed to be called Masinag Station).
The bike station is just across from the Line 2 Antipolo Station (what was supposed to be called Masinag Station).
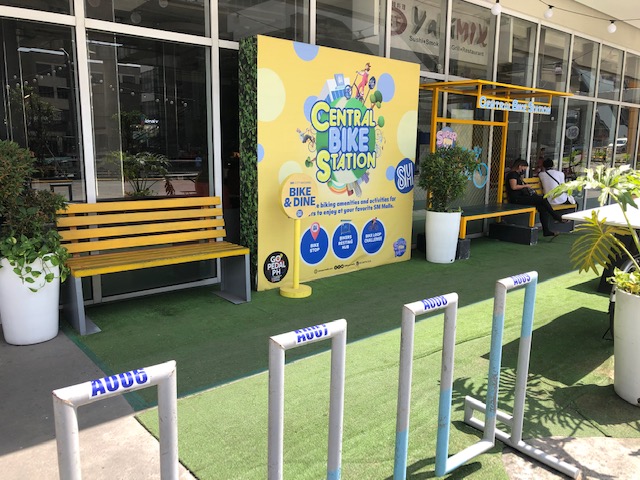 The central bike station also has benches for those who might want a rest and tables for those who want to “bike and dine”.
The central bike station also has benches for those who might want a rest and tables for those who want to “bike and dine”.
–
On the impacts of bicycle use
I’ve probably read a lot of posts on social media advocating for bicycle use. Here is another article that provides us with evidence about the impacts of cycling on travel, emissions and health:
Timmer, J. (August 20, 2022) “Here’s What Happens When Countries Use Bikes to Fight Emissions,” Wired, https://www.wired.com/story/bike-more-curb-global-emissions/ [Last accessed: 8/24/2022]
To quote from the article:
“Globally, adopting a Danish level of bicycle use would reduce annual emissions of CO2 by 414 million metric tons, approximately equivalent to the UK’s emissions in 2015. Boosting that to a Dutch level would eliminate nearly 700 million metric tons, or most of the emissions from Germany in that year.
The researchers also noted that countries like the Netherlands and Denmark have much lower rates of obesity than their peer countries. Based on the known health risks there, they estimate that, globally, we’re already avoiding 170,000 deaths annually due to cycling. Expanding this globally, they found that Denmark-equivalent bicycle use would prevent 430,000 deaths per year. Dutch levels of cycling would prevent 780,000 deaths.
That said, the vulnerability of cyclists to cars poses its own lethal risks. But these aren’t anywhere close to outweighing the benefits from exercise and lower obesity. (They’d add about 90,000 and 160,000 additional deaths per year for the two levels of use.) And if fewer drivers are using cars, there’s a chance that those numbers would come in even lower.
It’s worth noting that these numbers almost certainly underestimate the benefits of shifting to bikes. Bicycles use far fewer resources to produce, and they last longer than most cars. Maintenance is likely to be far less resource-intensive as well. So simply focusing on the use of the bike omits a lot of things that would show up in a detailed life-cycle analysis.
The researchers are certainly correct that there are a lot of locations where weather makes cycling a less-than-ideal option—and the range of places where heat makes it a positively dangerous option is expanding in our changing climate.
But some of the other issues are less severe than they might appear at first. For example, the advent of bicycles with electric assist means that hilly locales aren’t necessarily the barrier they might have been a decade ago. And while a number of countries have large open spaces where cars will remain a necessity, the trend toward urbanization means that most people in those countries will live in places where cycling can be made an option.
So, the biggest barrier is likely to remain the social will to rethink transportation.”
Indeed, social will (as well as political will) is perhaps the biggest barrier in our country. Many people may not agree but the evidence for this is so clear and obvious that one has to be naive or oblivious to not see it. How else will one explain people sticking to their cars and more readily shifting to motorcycles rather than the bicycle. Of course, there are other factors to be considered and the article actually cites wealth and geography as strong prerequisites in developing a cycling culture. We need to do much more to determine where interventions are needed including land use planning and land development as well as the provision of affordable housing closer to workplaces, schools, shops and other places of interest (Hello 10- or 15-minute cities!).
–
Bike lanes at the UP Diliman campus – Part 2
The bike lanes in UP Diliman are not limited to the Academic Oval. There are now also bike lanes along other major roads including Magsaysay Avenue, which is road immediately after the portal at the Asian Center and allowing direct entrance and exit via Katipunan Avenue (C-5). The bike lanes are along either side of Magsaysay Avenue and are of Class II – Type B (separated bike lanes) but there are no LED markers that are ideally placed along the delineation for the bike lanes.
 Painted bike lanes along Magsaysay Avenue, which is the road behind Malcolm and Melchor Halls. To the left is the Department of Mechanical Engineering Building and the Computer Center. To the right is the Resilience Institute.
Painted bike lanes along Magsaysay Avenue, which is the road behind Malcolm and Melchor Halls. To the left is the Department of Mechanical Engineering Building and the Computer Center. To the right is the Resilience Institute.
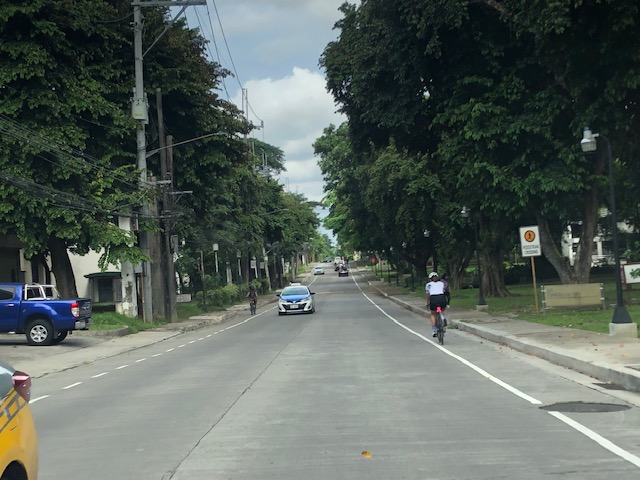 To the right is what used to be the Chemical Engineering Lab behind Melchor Hall. To the right is the Ipil and Yakal Dormitories.
To the right is what used to be the Chemical Engineering Lab behind Melchor Hall. To the right is the Ipil and Yakal Dormitories.
–
